Pioglitazone Represents an Effective Therapeutic Target in Preventing Oxidative/Inflammatory Cochlear Damage Induced by Noise Exposure
- PMID: 30349478
- PMCID: PMC6187064
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01103
Pioglitazone Represents an Effective Therapeutic Target in Preventing Oxidative/Inflammatory Cochlear Damage Induced by Noise Exposure
Abstract
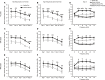
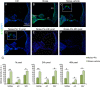
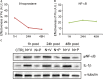
Recent progress in hearing loss research has provided strong evidence for the imbalance of cellular redox status and inflammation as common predominant mechanisms of damage affecting the organ of Corti including noise induced hearing loss. The discovery of a protective molecule acting on both mechanisms is challenging. The thiazolidinediones, a class of antidiabetic drugs including pioglitazone and rosiglitazone, have demonstrated diverse pleiotrophic effects in many tissues where they exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, tissue protective effects and regulators of redox balance acting as agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). They are members of the family of ligand regulated nuclear hormone receptors that are also expressed in several cochlear cell types, including the outer hair cells. In this study, we investigated the protective capacity of pioglitazone in a model of noise-induced hearing loss in Wistar rats and the molecular mechanisms underlying this protective effects. Specifically, we employed a formulation of pioglitazone in a biocompatible thermogel providing rapid, uniform and sustained inner ear drug delivery via transtympanic injection. Following noise exposure (120 dB, 10 kHz, 1 h), different time schedules of treatment were employed: we explored the efficacy of pioglitazone given immediately (1 h) or at delayed time points (24 and 48 h) after noise exposure and the time course and extent of hearing recovery were assessed. We found that pioglitazone was able to protect auditory function at the mid-high frequencies and to limit cell death in the cochlear basal/middle turn, damaged by noise exposure. Immunofluorescence and western blot analysis provided evidence that pioglitazone mediates both anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects by decreasing NF-κB and IL-1β expression in the cochlea and opposing the oxidative damage induced by noise insult. These results suggest that intratympanic pioglitazone can be considered a valid therapeutic strategy for attenuating noise-induced hearing loss and cochlear damage, reducing inflammatory signaling and restoring cochlear redox balance.
Keywords: PPAR agonist; acoustic trauma; antinflammatory; antioxidant; audiology; personalized medicine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid: in vivo evidences in a model of noise-induced hearing loss.Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Sep;143:111555. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111555. Epub 2020 Jul 5. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32640333
-
Effects of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR)-γ and -α agonists on cochlear protection from oxidative stress.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 28;12(11):e0188596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188596. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29182629 Free PMC article.
-
Styrene enhances the noise induced oxidative stress in the cochlea and affects differently mechanosensory and supporting cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Dec;101:211-225. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.10.014. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27769922
-
Inner Ear Hair Cell Protection in Mammals against the Noise-Induced Cochlear Damage.Neural Plast. 2018 Jul 15;2018:3170801. doi: 10.1155/2018/3170801. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 30123244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting dysregulation of redox homeostasis in noise-induced hearing loss: Oxidative stress and ROS signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 May 1;135:46-59. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.02.022. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30802489 Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT3 promotes auditory function in young adult FVB/nJ mice but is dispensable for hearing recovery after noise exposure.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 13;15(7):e0235491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235491. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32658908 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan Attenuates Kanamycin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 24;22(23):12716. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312716. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884516 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid imaging changes and serum IL-1β, sICAM-1, and sVAP-1 levels in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 9;10(1):21494. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78516-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33299063 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired sensorineural hearing loss, oxidative stress, and microRNAs.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Sep 1;20(9):2513-2519. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00579. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39314173 Free PMC article.
-
Reassessment of Pioglitazone for Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 16;15:666958. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.666958. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34220427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnum C. J., Tansey M. J. (2010). “Modeling neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease,” in Progress in Brain Research Vol. 184 eds Kerkhof G. A., Dongen H. P. A. Van. (London: Elsevier; ), 113–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

