Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Plant Hormone Signaling
- PMID: 30349547
- PMCID: PMC6187979
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01387
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Plant Hormone Signaling
Abstract
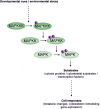
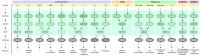
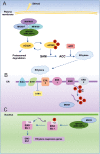
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) modules play key roles in the transduction of environmental and developmental signals through phosphorylation of downstream signaling targets, including other kinases, enzymes, cytoskeletal proteins or transcription factors, in all eukaryotic cells. A typical MAPK cascade consists of at least three sequentially acting serine/threonine kinases, a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK), a MAP kinase kinase (MAPKK) and finally, the MAP kinase (MAPK) itself, with each phosphorylating, and hence activating, the next kinase in the cascade. Recent advances in our understanding of hormone signaling pathways have led to the discovery of new regulatory systems. In particular, this research has revealed the emerging role of crosstalk between the protein components of various signaling pathways and the involvement of this crosstalk in multiple cellular processes. Here we provide an overview of current models and mechanisms of hormone signaling with a special emphasis on the role of MAPKs in cell signaling networks. One-sentence summary: In this review we highlight the mechanisms of crosstalk between MAPK cascades and plant hormone signaling pathways and summarize recent findings on MAPK regulation and function in various cellular processes.
Keywords: MAP kinase cascade; abscisic acid; auxin; brassinosteroids; ethylene; gibberellin; jasmonic acid; salicilic acid.
Figures



References
-
- Agrawal G. K., Tamogami S., Iwahashi H., Agrawal V. P., Rakwal R. (2003b). Transient regulation of jasmonic acid-inducible rice MAP kinase gene OsBWMK1 by diverse biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 41 355–361. 10.1016/S0981-9428(03)00030-5 - DOI
-
- Ahlfors R., Macioszek V., Rudd J., Brosche M., Schlichting R., Scheel D., et al. (2004). Stress hormone-independent activation and nuclear translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis thaliana during ozone exposure. Plant J. 40 512–522. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02229.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

