Accurate Prediction of ncRNA-Protein Interactions From the Integration of Sequence and Evolutionary Information
- PMID: 30349558
- PMCID: PMC6186793
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00458
Accurate Prediction of ncRNA-Protein Interactions From the Integration of Sequence and Evolutionary Information
Abstract
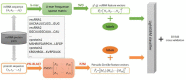
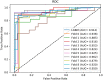
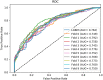
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes including gene expression and post-transcriptional gene regulation. The biological function of ncRNA is mostly realized by binding with related proteins. Therefore, an accurate understanding of interactions between ncRNA and protein has a significant impact on current biological research. The major challenge at this stage is the waste of a great deal of redundant time and resource consumed on classification in traditional interaction pattern prediction methods. Fortunately, an efficient classifier named LightGBM can solve this difficulty of long time consumption. In this study, we employed LightGBM as the integrated classifier and proposed a novel computational model for predicting ncRNA and protein interactions. More specifically, the pseudo-Zernike Moments and singular value decomposition algorithm are employed to extract the discriminative features from protein and ncRNA sequences. On four widely used datasets RPI369, RPI488, RPI1807, and RPI2241, we evaluated the performance of LGBM and obtained an superior performance with AUC of 0.799, 0.914, 0.989, and 0.762, respectively. The experimental results of 10-fold cross-validation shown that the proposed method performs much better than existing methods in predicting ncRNA-protein interaction patterns, which could be used as a useful tool in proteomics research.
Keywords: LightGBM; PSSM; Pseudo-Zernike moments; k-mers; ncRNA-protein interactions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Deep Learning Framework for Robust and Accurate Prediction of ncRNA-Protein Interactions Using Evolutionary Information.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Jun 1;11:337-344. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 29858068 Free PMC article.
-
RPITER: A Hierarchical Deep Learning Framework for ncRNA⁻Protein Interaction Prediction.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 1;20(5):1070. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051070. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30832218 Free PMC article.
-
RPI-SE: a stacking ensemble learning framework for ncRNA-protein interactions prediction using sequence information.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Feb 18;21(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3406-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32070279 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Methods for Predicting ncRNA-protein Interactions.Med Chem. 2017;13(6):515-525. doi: 10.2174/1573406413666170510102405. Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28494725 Review.
-
Versatile interactions and bioinformatics analysis of noncoding RNAs.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Sep 27;20(5):1781-1794. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby050. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29939215 Review.
Cited by
-
LPI-IBNRA: Long Non-coding RNA-Protein Interaction Prediction Based on Improved Bipartite Network Recommender Algorithm.Front Genet. 2019 Apr 18;10:343. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00343. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31057602 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Model in Predicting Sarcopenia in Crohn's Disease Based on Simple Clinical and Anthropometric Measures.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 30;20(1):656. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010656. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612977 Free PMC article.
-
Development of machine learning model for diagnostic disease prediction based on laboratory tests.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 7;11(1):7567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87171-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33828178 Free PMC article.
-
A Hybrid Prediction Method for Plant lncRNA-Protein Interaction.Cells. 2019 May 30;8(6):521. doi: 10.3390/cells8060521. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31151273 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and Challenges of Predictive Approaches for the Non-coding RNA in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 14;13:890663. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.890663. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35498708 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Appel R., Fuchs T., Perona P. (2013). Quickly boosting decision trees, pruning underachieving features early, in International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning: 2013 (Atlanta, GA: ), III-594.
-
- Berman H. M., Westbrook J., Feng Z., Gilliland G., Bhat T. N., Weissig H., et al. (2000). The Protein Data Bank, 1999–. Int. Tables Crystallograp. 67, 675–684. 10.1107/97809553602060000722 - DOI
-
- Chen T., Guestrin C. (2016). XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. arXiv:1603.02754. 2016, 785–94.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

