Metal allergy patient treated by titanium implant denture: A case report with at least 4-year follow-up
- PMID: 30349710
- PMCID: PMC6186882
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.1753
Metal allergy patient treated by titanium implant denture: A case report with at least 4-year follow-up
Abstract
Patch testing with metal reagents was positive on female patient with history of metal hypersensitivity after dental treatment. All of the dental restorations with metal components were removed, and subsequent oral rehabilitation utilizing dental implants and metal-free prostheses was carried out. The treatments alleviate the presenting signs and symptoms.
Keywords: case study; metal allergy; patch test; titanium implant.
Figures
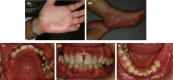
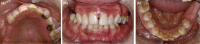
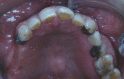


Similar articles
-
Titanium Allergy Caused by Dental Implants: A Systematic Literature Review and Case Report.Materials (Basel). 2021 Sep 12;14(18):5239. doi: 10.3390/ma14185239. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34576463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-sectional observational study exploring clinical risk of titanium allergy caused by dental implants.J Prosthodont Res. 2018 Oct;62(4):426-431. doi: 10.1016/j.jpor.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Prosthodont Res. 2018. PMID: 29673741
-
[The application of titanium prostheses to a patient with metal allergy].Nihon Hotetsu Shika Gakkai Zasshi. 2007 Jul;51(3):604-7. doi: 10.2186/jjps.51.604. Nihon Hotetsu Shika Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17957844 Japanese.
-
Full-mouth oral rehabilitation in a titanium allergy patient using zirconium oxide dental implants and zirconium oxide restorations. A case report from an ongoing clinical study.Eur J Esthet Dent. 2010 Summer;5(2):190-203. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2010. PMID: 20589262
-
Oral health-related quality of life of patients rehabilitated with fixed and removable implant-supported dental prostheses.Periodontol 2000. 2022 Feb;88(1):201-237. doi: 10.1111/prd.12419. Periodontol 2000. 2022. PMID: 35103325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrospun PVP Fibers as Carriers of Ca2+ Ions to Improve the Osteoinductivity of Titanium-Based Dental Implants.Molecules. 2024 Sep 3;29(17):4181. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174181. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39275029 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm Formation on the Surface of (Poly)Ether-Ether-Ketone and In Vitro Antimicrobial Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy on Peri-Implant Mucositis.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;13(6):940. doi: 10.3390/polym13060940. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803736 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium salts tested in reconstructed human skin with integrated MUTZ-3-derived Langerhans cells show an irritant rather than a sensitizing potential.Contact Dermatitis. 2020 Nov;83(5):337-346. doi: 10.1111/cod.13666. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Contact Dermatitis. 2020. PMID: 32677096 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of colorectal cancer cases with metal allergy.Surg Today. 2023 Jul;53(7):753-761. doi: 10.1007/s00595-023-02643-7. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Surg Today. 2023. PMID: 36757618
-
Titanium Allergy Caused by Dental Implants: A Systematic Literature Review and Case Report.Materials (Basel). 2021 Sep 12;14(18):5239. doi: 10.3390/ma14185239. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34576463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raap U, Stiesch M, Kapp A. Contact allergy to dental materials. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10:391‐396. - PubMed
-
- Wataha JC, Lockwood PE, Khajotia SS, Turner R. Effect of pH on element release from dental casting alloys. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;80:691‐698. - PubMed
-
- Elshahawy W, Watanabe I, Koike M. Elemental ion release from four different fixed prosthodontic materials. Dent Mater. 2009;25:976‐998. - PubMed
-
- Bishara SE, Barrett RD, Selim MI. Biodegradation of orthodontic appliances. Part II. Changes in the blood level of nickel. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993;103:115‐119. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

