Transgenerational inheritance of behavioral and metabolic effects of paternal exposure to traumatic stress in early postnatal life: evidence in the 4th generation
- PMID: 30349741
- PMCID: PMC6190267
- DOI: 10.1093/eep/dvy023
Transgenerational inheritance of behavioral and metabolic effects of paternal exposure to traumatic stress in early postnatal life: evidence in the 4th generation
Abstract
In the past decades, evidence supporting the transmission of acquired traits across generations has reshaped the field of genetics and the understanding of disease susceptibility. In humans, pioneer studies showed that exposure to famine, endocrine disruptors or trauma can affect descendants, and has led to a paradigm shift in thinking about heredity. Studies in humans have however been limited by the low number of successive generations, the different conditions that can be examined, and the lack of mechanistic insight they can provide. Animal models have been instrumental to circumvent these limitations and allowed studies on the mechanisms of inheritance of environmentally induced traits across generations in controlled and reproducible settings. However, most models available today are only intergenerational and do not demonstrate transmission beyond the direct offspring of exposed individuals. Here, we report transgenerational transmission of behavioral and metabolic phenotypes up to the 4th generation in a mouse model of paternal postnatal trauma (MSUS). Based on large animal numbers (up to 124 per group) from several independent breedings conducted 10 years apart by different experimenters, we show that depressive-like behaviors are transmitted to the offspring until the third generation, and risk-taking and glucose dysregulation until the fourth generation via males. The symptoms are consistent and reproducible, and persist with similar severity across generations. These results provide strong evidence that adverse conditions in early postnatal life can have transgenerational effects, and highlight the validity of MSUS as a solid model of transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.
Keywords: 3rd and 4th generation; behavior; early-life trauma; epigenetic inheritance; mouse model; transgenerational.
Figures
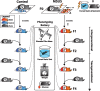

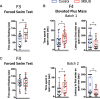

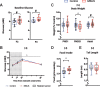
References
-
- Bohacek J, Mansuy IM.. Molecular insights into transgenerational non-genetic inheritance of acquired behaviours. Nat Rev Genet 2015;16:641–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

