Accuracy of Pre- and Postcontrast, 3 T Indirect MR Arthrography Compared with Wrist Arthroscopy in the Diagnosis of Wrist Ligament Injuries
- PMID: 30349750
- PMCID: PMC6196091
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1661419
Accuracy of Pre- and Postcontrast, 3 T Indirect MR Arthrography Compared with Wrist Arthroscopy in the Diagnosis of Wrist Ligament Injuries
Abstract
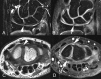
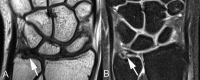
Background Magnetic resonance (MR) is the most important imaging technique to assess intra-articular pathology of the wrist. Among various MR imaging protocols, the diagnostic performance of indirect MR arthrography needs further investigation. Purpose The purpose of this study was to assess the diagnostic performance of pre- and postcontrast, 3 T indirect MR arthrography in the diagnosis of scapholunate intrinsic ligament (SLIL) and triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injuries, using wrist arthroscopy as reference standard. Patients and Methods We retrospectively evaluated consecutive patients with suspected SLIL or TFCC injury, who had indirect MR arthrography done before arthroscopy. Images were assessed independently by two senior radiologists. Results Arthroscopy of the 53 wrists demonstrated 16 Geissler stages II and III partial tears and 6 stage IV total SLIL ruptures. Central perforation of the TFCC was found in 24 wrists, and 12 wrists had an ulnar class 1B lesion. To detect any SLIL tear, accuracy was higher for the two observers using postcontrast indirect MR arthrography (0.77 and 0.72) than for precontrast MR imaging (0.60 and 0.60). No difference was found for total SLIL ruptures "0.85 and 0.89" versus "0.85 and 0.89." To diagnose class 1B TFCC injuries, accuracy was higher using postcontrast indirect MR arthrography (0.85 and 0.75) than for precontrast MR imaging (0.70 and 0.72). No difference in accuracy was demonstrated for TFCC central tears "0.75 and 0.75" versus "0.70 and 0.77." Conclusion Postcontrast images at 3 T indirect MR arthrography, compared with precontrast images, have an improved diagnostic performance for the overall detection of SLIL injuries and as well as class 1B TFCC tears. Level of Evidence This is a Level II, diagnostic study.
Keywords: MR imaging; arthroscopy; diagnostic performance; indirect MR arthrography; scapholunate ligament; triangular fibrocartilage complex; wrist.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrinsic ligament and triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears of the wrist: comparison of isovolumetric 3D-THRIVE sequence MR arthrography and conventional MR image at 3 T.Magn Reson Imaging. 2013 Feb;31(2):221-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.024. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013. PMID: 22959873
-
[Direct MR arthrography of the wrist- value in detecting complete and partial defects of intrinsic ligaments and the TFCC in comparison with arthroscopy].Rofo. 2003 Nov;175(11):1515-24. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-43404. Rofo. 2003. PMID: 14610703 German.
-
Wrist Traction During MR Arthrography Improves Detection of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex and Intrinsic Ligament Tears and Visibility of Articular Cartilage.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016 Jan;206(1):155-61. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14948. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016. PMID: 26700348
-
Ligamentous injuries of the wrist.Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2008 Dec;12(4):359-77. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1100642. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2008. PMID: 19016398 Review.
-
MDCT arthrography or MR arthrography for imaging the wrist joint?Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2009 Mar;13(1):39-54. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1202244. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19235671 Review.
Cited by
-
MRI of wrist ligament trauma was similar at 7 T and 3 T with arthroscopy as a reference standard.Eur Radiol. 2025 May 8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11656-4. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40341973
-
Improved diagnostic accuracy for ulnar-sided TFCC lesions with radial reformation of 3D sequences in wrist MR arthrography.Eur Radiol. 2021 Dec;31(12):9399-9407. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08024-3. Epub 2021 May 18. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34003353 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist and hand.Pol J Radiol. 2020 Aug 26;85:e461-e488. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2020.99034. eCollection 2020. Pol J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32999697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of radial multiplanar reconstructions for assessment of triangular fibrocartilage complex injury in CT arthrography of the wrist.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 May 7;21(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03321-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32381000 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic injury of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)-a refinement to the Palmer classification by using high-resolution 3-T MRI.Skeletal Radiol. 2020 Oct;49(10):1567-1579. doi: 10.1007/s00256-020-03438-4. Epub 2020 May 5. Skeletal Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32372253
References
-
- Berger R A. The ligaments of the wrist. A current overview of anatomy with considerations of their potential functions. Hand Clin. 1997;13(01):63–82. - PubMed
-
- Zanetti M, Saupe N, Nagy L. Role of MR imaging in chronic wrist pain. Eur Radiol. 2007;17(04):927–938. - PubMed
-
- Anderson M L, Skinner J A, Felmlee J P, Berger R A, Amrami K K. Diagnostic comparison of 1.5 Tesla and 3.0 Tesla preoperative MRI of the wrist in patients with ulnar-sided wrist pain. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(07):1153–1159. - PubMed
-
- Hafezi-Nejad N, Carrino J A, Eng J et al.Scapholunate interosseous ligament tears: diagnostic performance of 1.5 T, 3 T MRI, and MR arthrography-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad Radiol. 2016;23(09):1091–1103. - PubMed
-
- Smith T O, Drew B, Toms A P, Jerosch-Herold C, Chojnowski A J. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance arthrography for triangular fibrocartilaginous complex injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(09):824–832. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

