Curcumin-loaded chitosan-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles potentially enhanced Aβ 42 phagocytosis and modulated macrophage polarization in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30350003
- PMCID: PMC6197340
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-018-2759-z
Curcumin-loaded chitosan-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles potentially enhanced Aβ 42 phagocytosis and modulated macrophage polarization in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
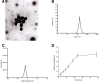
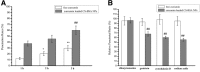
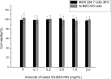
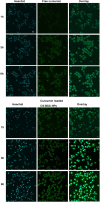
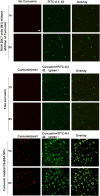
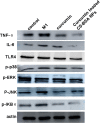
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder in the elderly population. In the treatment of AD, some obstacles, including drug penetration difficulty through the blood-brain barrier (BBB), inadequate clearance of the Aβ peptide, and the massive release of inflammatory factors, must be urgently overcome. To solve these problems, we developed special and novel nanoparticles (NPs) made of chitosan (CS) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) to enhance the penetration of drugs through the BBB. Curcumin as a potent anti-inflammatory agent was used to increase the phagocytosis of the Aβ peptide. The results demonstrated that curcumin-loaded CS-BSA NPs effectively increased drug penetration through the BBB, promoted the activation of microglia, and further accelerated the phagocytosis of the Aβ peptide. Furthermore, curcumin-loaded CS-BSA NPs inhibited the TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway and further downregulated M1 macrophage polarization. This study suggested that curcumin-loaded CS-BSA NPs hold the potential to enhance Aβ 42 phagocytosis through modulating macrophage polarization in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ peptide; Blood–brain barrier; Curcumin; Nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PLGA nanoparticles modified with a BBB-penetrating peptide co-delivering Aβ generation inhibitor and curcumin attenuate memory deficits and neuropathology in Alzheimer's disease mice.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 15;8(46):81001-81013. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20944. eCollection 2017 Oct 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29113362 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Curcumin loaded nanoparticles engineered for Blood-Brain Barrier crossing and able to disrupt Abeta aggregates.Int J Pharm. 2017 Jun 30;526(1-2):413-424. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 May 8. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28495580
-
Glucose-modified BSA/procyanidin C1 NPs penetrate the blood-brain barrier and alleviate neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease models.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 1):131739. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131739. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38657920
-
Examining the potential clinical value of curcumin in the prevention and diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.Br J Nutr. 2016 Feb 14;115(3):449-65. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515004687. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26652155 Review.
-
Macrophage plasticity, polarization and function in response to curcumin, a diet-derived polyphenol, as an immunomodulatory agent.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Apr;66:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30660832 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanocarrier-mediated curcumin delivery: An adjuvant strategy for CNS disease treatment.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Nov;248(22):2151-2166. doi: 10.1177/15353702231211863. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 38058006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Nanocarrier-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Targeting: A Current Review of Literature.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Nov 11;16:7517-7533. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S333657. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34795481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Product-based Nanomedicine: Recent Advances and Issues for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(8):1498-1518. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666211217163540. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34923947 Free PMC article.
-
Marine-derived polysaccharides: the potential agents against neurodegenerative diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1506789. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1506789. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39744139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-assembly of Organic Nanomaterials and Biomaterials: The Bottom-Up Approach for Functional Nanostructures Formation and Advanced Applications.Materials (Basel). 2020 Feb 26;13(5):1048. doi: 10.3390/ma13051048. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32110877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lambert MP, Barlow AK, Chromy BA, Edwards C, Freed R, Liosatos M, Morgan TE, Rozovsky I, Trommer B, Viola KL, Wals P, Zhang C, Finch CE, Krafft GA, Klein WL. Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1998;95(11):6448–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6448. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

