An In Vitro Study of the Effect of Cytotoxic Triorganotin Dimethylaminophenylazobenzoate Complexes on Red Blood Cells
- PMID: 30350012
- PMCID: PMC6244762
- DOI: 10.1007/s00232-018-0051-x
An In Vitro Study of the Effect of Cytotoxic Triorganotin Dimethylaminophenylazobenzoate Complexes on Red Blood Cells
Abstract
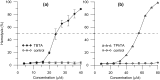
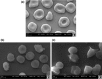
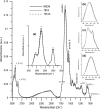
Interactions of tributyltin (TBTA) and triphenyltin (TPhTA) 2-[4 (dimethylamino)phenylazo]benzoates, showing promising cytostatic activity against tumor cells, with erythrocytes and with erythrocyte membranes and model lipid membranes have been investigated. The effect of TBTA and TPhTA on the erythrocyte and its model membrane was investigated by the microscopic and spectroscopic methods. Interaction of tin complexes with the membrane was determined on the basis of hemolytic activity, changes induced in the shape of erythrocytes, as well as physicochemical parameters of the membrane, such as fluidity. The studies showed that the compounds in higher concentration induce hemolysis; however, TBTA is more toxic than TPhTA. Both TBTA and TPhTA induce morphological alterations in red blood cells-from discocytes to spherocytes and from discocytes to echinocytes. The results suggest that investigated complexes interact with the erythrocyte membrane, change its properties, and probably locate themselves in the hydrophilic part of the membrane, which agrees with conclusions drawn from investigation of erythrocyte membranes and model lipid membranes with the help of fluorescence and infrared spectroscopy.
Keywords: Cell membrane; Erythrocyte; Hemolytic activity; Microscopy; Spectroscopy; Triorganotin compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human and Animal Participants
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The location of organotins within the erythrocyte membrane in relation to their toxicity.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2012 Apr;78:232-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.027. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2012. PMID: 22153305
-
Effect of triorganotin compounds on membrane permeability.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1720(1-2):137-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.12.005. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16472558
-
Molecular mechanism of action of chlorogenic acid on erythrocyte and lipid membranes.Mol Membr Biol. 2015;32(2):46-54. doi: 10.3109/09687688.2015.1031833. Epub 2015 May 6. Mol Membr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25945513
-
Triorganotin as a compound with potential reproductive toxicity in mammals.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011 Sep;44(9):958-65. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2011007500110. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011. PMID: 21876874 Review.
-
Membrane fluidity of blood cells.Haematologia (Budap). 1996;27(3):109-27. Haematologia (Budap). 1996. PMID: 14653448 Review.
Cited by
-
Solid Self-Nano Emulsifying Nanoplatform Loaded with Tamoxifen and Resveratrol for Treatment of Breast Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 18;14(7):1486. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071486. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890384 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a Palladium(II)-tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine Complex on Normal Cells: Toxicity and Membrane Interaction.Molecules. 2025 Jan 22;30(3):476. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030476. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942580 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of 4'-methylflavonoids with biological membranes, liposomes, and human albumin.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 6;11(1):16003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95430-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34362978 Free PMC article.
-
Chemo-enzymatic synthesis and biological activity evaluation of propenylbenzene derivatives.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 26;14:1223123. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1223123. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37434714 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Distigmasterol-Modified Acylglycerols on the Fluidity and Phase Transition of Lipid Model Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;12(11):1054. doi: 10.3390/membranes12111054. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baile MB, Kolhe NS, Deotarse PP, Jain AS, Kulkarni AA. Metal ion complex—potential anticancer drug-a review. IJPRR. 2015;4(8):59–66.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

