Acetone/Isopropanol Photoinitiating System Enables Tunable Disulfide Reduction and Disulfide Mapping via Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 30350608
- PMCID: PMC6310128
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04019
Acetone/Isopropanol Photoinitiating System Enables Tunable Disulfide Reduction and Disulfide Mapping via Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
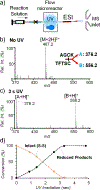
Herein, we report the development of a new photochemical system which enables rapid and tunable disulfide bond reduction and its application in disulfide mapping via online coupling with mass spectrometry (MS). Acetone, a clean and electrospray ionization (ESI) compatible solvent, is used as the photoinitiator (1% volume) in the solvent system consisting of 1:1 alkyl alcohol and water. Under ultraviolet (UV) irradiation (∼254 nm), the acetone/alcohol system produces hydroxyalkyl radicals, which are responsible for disulfide bond cleavage in peptides. Acetone/isopropanol is most suitable for optimizing the disulfide reduction products, leading to almost complete conversion in less than 5 s when the reaction is conducted in a flow microreactor. The flow microreactor device not only facilitates direct coupling with ESI-MS but also allows fine-tuning of the extent of disulfide reduction by varying the UV exposure time. Near full sequence coverage for peptides consisting of intra- or interchain disulfide bonds has been achieved from complete disulfide reduction and online tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) via low energy collision-induced dissociation. Coupling different degrees of partial disulfide reduction with ESI-MS/MS allows disulfide mapping as demonstrated for characterizing the three disulfide bonds in insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
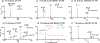





References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

