The Effect of School Closure on Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Transmission in Singapore: A Modeling Approach
- PMID: 30350767
- PMCID: PMC6283473
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0099
The Effect of School Closure on Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Transmission in Singapore: A Modeling Approach
Abstract
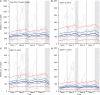
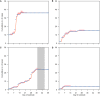
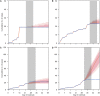
Singapore implements a school closure policy for institutional hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) outbreaks, but there is a lack of empirical evidence on the effect of closure on HFMD transmission. We conducted a retrospective analysis of 197,207 cases of HFMD over the period 2003-2012 at the national level and of 57,502 cases in 10,080 institutional outbreaks over the period 2011-2016 in Singapore. The effects of school closure due to 1) institutional outbreaks, 2) public holidays, and 3) school vacations were assessed using a Bayesian time series modeling approach. School closure was associated with a reduction in HFMD transmission rate. During public holidays, average numbers of secondary cases having onset the week after dropped by 53% (95% credible interval 44-62%), and during school vacations, the number of secondary cases dropped by 7% (95% credible interval 3-10%). Schools being temporarily closed in response to an institutional outbreak reduced the average number of new cases by 1,204 (95% credible interval 1,140-1,297). Despite the positive effect in reducing transmission, the effect of school closure is relatively small and may not justify the routine use of this measure.
Figures

References
-
- Ang LW, Koh BK, Chan KP, Chua LT, James L, Goh KT, 2009. Epidemiology and control of hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore, 2001–2007. Ann Acad Med Singapore 38: 106–112. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) , 2012. Notes from the field: severe hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A6-Alabama, Connecticut, California, and Nevada, November 2011–February 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 61: 213–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

