Endocytosis Pathways of Endothelial Cell Derived Exosomes
- PMID: 30351959
- PMCID: PMC6465166
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00765
Endocytosis Pathways of Endothelial Cell Derived Exosomes
Abstract
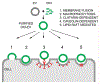
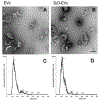
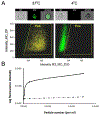
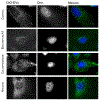
Nanosized extracellular vesicles (EVs) possess the natural machinery needed to enter selectively and transmit complex molecular messages efficiently into targeted cells. The intracellular fate of the vesicular cargos depends on the route of internalization. Therefore, understanding the mechanism of attachment and subsequent intake of these vesicles (before and after exerting any modification) is imperative. Here the extent of communication, the uptake kinetics, and the pathways of endothelial EVs into endothelial cells in the presence of specific pharmacological inhibitors were assessed by imaging flow cytometry. The results showed that the uptake of endothelial EVs into endothelial cells was largely an energy-dependent process using predominantly a receptor-mediated, clathrin-dependent pathway.
Keywords: endocytosis; endothelial cells; exosome; extracellular vesicles; nanomedicine.
Figures

References
-
- Théry C, Boussac M, Véron P, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Raposo G, Garin J and Amigorena S. Proteomic Analysis of Dendritic Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Secreted Subcellular Compartment Distinct from Apoptotic Vesicles. J. Immunol 2001, 166(12), 7309–7318. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow YQ, Yin HF, Betts C, Lakhai S, Wood MJA Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes, Nature Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

