Hepatic hepcidin/intestinal HIF-2α axis maintains iron absorption during iron deficiency and overload
- PMID: 30352047
- PMCID: PMC6307944
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI122359
Hepatic hepcidin/intestinal HIF-2α axis maintains iron absorption during iron deficiency and overload
Abstract
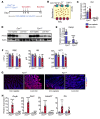
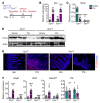
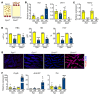
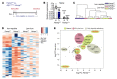
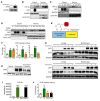
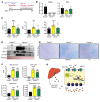
Iron-related disorders are among the most prevalent diseases worldwide. Systemic iron homeostasis requires hepcidin, a liver-derived hormone that controls iron mobilization through its molecular target ferroportin (FPN), the only known mammalian iron exporter. This pathway is perturbed in diseases that cause iron overload. Additionally, intestinal HIF-2α is essential for the local absorptive response to systemic iron deficiency and iron overload. Our data demonstrate a hetero-tissue crosstalk mechanism, whereby hepatic hepcidin regulated intestinal HIF-2α in iron deficiency, anemia, and iron overload. We show that FPN controlled cell-autonomous iron efflux to stabilize and activate HIF-2α by regulating the activity of iron-dependent intestinal prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes. Pharmacological blockade of HIF-2α using a clinically relevant and highly specific inhibitor successfully treated iron overload in a mouse model. These findings demonstrate a molecular link between hepatic hepcidin and intestinal HIF-2α that controls physiological iron uptake and drives iron hyperabsorption during iron overload.
Keywords: Gastroenterology; hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
At the crossroads of oxygen and iron sensing: hepcidin control of HIF-2α.J Clin Invest. 2019 Jan 2;129(1):72-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI125509. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30530987 Free PMC article.
-
Iron and oxygen sensing: discovering intricate links.Kidney Int. 2019 Mar;95(3):482-484. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.01.003. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 30784652 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

