Associations of canopy leaf traits with SNP markers in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. durum (Desf.))
- PMID: 30352102
- PMCID: PMC6198983
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206226
Associations of canopy leaf traits with SNP markers in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. durum (Desf.))
Abstract
The canopy leaves including the top three, i.e., the flag, the 2nd and 3rd from the top, are important for photosynthesis and grain yield of wheat. Molecular markers associated with traits of these leaves should be helpful for the high-yielding breeding. In this study, 1366 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) markers covering the whole genome of durum wheat were used to genotype 150 cultivars collected from 46 countries and regions in the world. Leaf length, leaf width and chlorophyll content of the top three leaves were measured, respectively, in three consecutive years. Association analyses were performed on the leaf traits and SNP markers. A total of 120 SNP marker associations were detected on 13 of the 14 chromosomes. Among these markers, 83 were associated with the canopy leaf traits, 10 with 1000-grain weight, and 29 with kernel number per spike. This study is helpful for better understanding the potential and genetic basis of functional leaves, and facilitates pyramiding of the favorable alleles using marker assisted selection for ideal plant-type and high photosynthesis efficiency in durum wheat breeding.
Conflict of interest statement
We have the following interest. Junhua Peng is employed by China National Seed Group Co. Ltd. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures
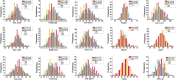
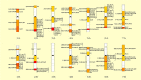
Similar articles
-
Association of Agronomic Traits with SNP Markers in Durum Wheat (Triticum turgidum L. durum (Desf.)).PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0130854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130854. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26110423 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic architecture of grain yield in bread wheat based on genome-wide association studies.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Apr 29;19(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1781-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31035920 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity and Association Mapping for Agromorphological and Grain Quality Traits of a Structured Collection of Durum Wheat Landraces Including subsp. durum, turgidum and diccocon.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 15;11(11):e0166577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166577. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27846306 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mapping and Genomics of Grain Yield in Durum Wheat: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 24;21(19):7021. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197021. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32987666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Trait Loci Conferring Leaf Rust Resistance in Hexaploid Wheat.Phytopathology. 2018 Dec;108(12):1344-1354. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-06-18-0208-RVW. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Phytopathology. 2018. PMID: 30211634 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Association of Stem Carbohydrate Accumulation and Remobilization during Grain Growth in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in Mediterranean Environments.Plants (Basel). 2021 Mar 12;10(3):539. doi: 10.3390/plants10030539. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809230 Free PMC article.
-
SNP-based association study of kernel architecture in a worldwide collection of durum wheat germplasm.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 14;15(2):e0229159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229159. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32059028 Free PMC article.
-
The allelopathy of horseweed with different invasion degrees in three provinces along the Yangtze River in China.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021 Mar;27(3):483-495. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-00962-y. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021. PMID: 33854278 Free PMC article.
-
A new major QTL for flag leaf thickness in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jun 24;22(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03694-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35751018 Free PMC article.
-
Association Analysis for Some Biochemical Traits in Wild Relatives of Wheat under Drought Stress Conditions.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 21;13(8):1491. doi: 10.3390/genes13081491. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green AJ, Berger G, Griffey C, Pitman R, Thomason W, Balota M, et al. Genetic yield improvement in soft red winter wheat in the Eastern United States from 1919 to 2009. Crop science. 2012;52:2097–2108.
-
- Li JH, Li GH, Zhang YG, Luo QR, Yang CD, Wang SH, et al. Effects of precise and quantitative cultivation on plant type and yield of rice in high altitude and cold ecological area. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 2009;42:3067–3077.
-
- Murthy KK, Singh M. Photosynthesis, chlorophyll content and ribulose diphosphate carboxylase activity in relation to yield in wheat genotypes. The Journal of Agricultural Science. 2009; 93:7.
-
- Li Z, Pinson SR, Stansel JW, Paterson AH. Genetic dissection of the source-sink relationship affecting fecundity and yield in rice (shape Oryza sativa L.). Molecular Breeding. 1998;4:419–426.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

