Therapeutic potential of carbonyl-scavenging carnosine derivative in metabolic disorders
- PMID: 30352430
- PMCID: PMC6264722
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI124304
Therapeutic potential of carbonyl-scavenging carnosine derivative in metabolic disorders
Abstract
Obesity and overnutrition increase levels of reactive sugar- and lipid-derived aldehydes called reactive carbonyl species (RCS). Increased tissue and circulating RCS levels have been tied to insulin resistance and inflammation, but previous pharmacological approaches to target RCS have had equivocal outcomes. In this issue of the JCI, Anderson et al. present evidence for the development and implementation of carnisonol, a compound that is biologically stable in vivo and shows impressive effects on improving metabolism and inflammation in rodent models of diet-induced obesity and metabolic dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
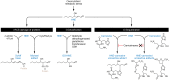
Comment on
-
A carnosine analog mitigates metabolic disorders of obesity by reducing carbonyl stress.J Clin Invest. 2018 Dec 3;128(12):5280-5293. doi: 10.1172/JCI94307. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30226473 Free PMC article.

