Predicting vitamin E and C consumption intentions and behaviors among factory workers based on protection motivation theory
- PMID: 30352557
- PMCID: PMC6199700
- DOI: 10.1186/s12199-018-0742-z
Predicting vitamin E and C consumption intentions and behaviors among factory workers based on protection motivation theory
Abstract
Background: Study of antioxidant vitamin consumption behavior, especially in high-risk groups with high exposure to toxic metals to reduce metal toxicity, is emphasized. This study aims to examine the structural relationships between knowledge, protection motivation theory constructs, and vitamin E and C consumption behavior among cement factory workers.
Methods: Protection motivation theory and food frequency questionnaires were completed by 420 factory workers. Data were subjected to structural equation modeling to examine associations between knowledge, protection motivation theory constructs, and vitamin E and C consumption behavior. Efficacy of current recommended models was also explored.
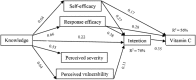
Results: Structural equation modeling showed high explained variance within the constructs of protection motivation theory for vitamin E and C consumption behavior and intention (56-76%). The overall fit of the structural models was acceptable for both vitamin E and C behavior. Knowledge, self-efficacy, response efficacy, and perceived vulnerability predicted intention, which in turn predicted vitamin consumption behavior. Significant relationships between knowledge and self-efficacy, response efficacy, perceived vulnerability, and perceived severity were also found, while self-efficacy and response efficacy showed significant relationships with vitamin E and C consumption behavior.
Conclusions: Considering that response efficacy, self-efficacy, and intention showed as strong predictors of vitamin E and C consumption behavior, specific attention should be paid to coping appraisals and intention when designing intervention plans. Additionally, establishing the predicting role of knowledge for protection motivation theory constructs and protective behaviors should be integrated into intervention programs.
Keywords: Protection motivation theory; Structural equation modeling; Vitamin C; Vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences ethics board (Number: Rec.ir.muk1395.70) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study on the basis of a procedure that is officially approved by the Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protection motivation theory in predicting intention to engage in protective behaviors against schistosomiasis among middle school students in rural China.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Oct 16;8(10):e3246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003246. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25329829 Free PMC article.
-
AIDS-related health behavior: coping, protection motivation, and previous behavior.J Behav Med. 1991 Oct;14(5):429-51. doi: 10.1007/BF00845103. J Behav Med. 1991. PMID: 1744908
-
Factors Associated with Tobacco Use among Iranian Adolescents: An Application of Protection Motivation Theory.Subst Use Misuse. 2018 Jul 29;53(9):1511-1518. doi: 10.1080/10826084.2017.1415356. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Subst Use Misuse. 2018. PMID: 29313745
-
The influence of antiobesity media content on intention to eat healthily and exercise: a test of the ordered protection motivation theory.J Obes. 2014;2014:954784. doi: 10.1155/2014/954784. Epub 2014 Nov 19. J Obes. 2014. PMID: 25505981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Social cognition correlates of self-management behaviors in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH): A meta-analytic review.Soc Sci Med. 2024 Jun;351:116968. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2024.116968. Epub 2024 May 11. Soc Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38759387 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Protection Motivation Theory on clinical factors, behavior change, and cardiovascular disease: An integrative review.Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024 Nov 13;7:100267. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2024.100267. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024. PMID: 39717156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting dietary management intention of patients with chronic kidney disease using protection motivation theory.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 18;20(3):e0320340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320340. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40100873 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting preventive behaviors of cardiovascular disease among oil industry workers based on health belief model.J Educ Health Promot. 2022 Oct 31;11:346. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_158_22. eCollection 2022. J Educ Health Promot. 2022. PMID: 36567991 Free PMC article.
-
Consumption Behaviour towards Branded Functional Beverages among Gen Z in Post-COVID-19 Times: Exploring Antecedents and Mediators.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;13(8):670. doi: 10.3390/bs13080670. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bermudez GM, Moreno M, Invernizzi R, Plá R, Pignata ML. Heavy metal pollution in topsoils near a cement plant: the role of organic matter and distance to the source to predict total and HCl-extracted heavy metal concentrations. Chemosphere. 2010;78:375–381. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babalola OO, Babajide S. Selected heavy metals and electrolyte levels in blood of workers and residents of industrial communities. Afr J Biochem Res. 2009;3:37–40.
-
- Salh DM, Mohammed SM, Salih LO. Some biochemical and hematological parameters among petroleum and cement factory workers in Sulaimaniyah city/Kurdistan/Iraq. Chem. Mater Res. 2014;6:29–32.
-
- Das K, Jargar KG, Hattiwale JH, Yendigeri SM, Das S, Dhundasi SA. Serum vitamin E (α-tocopherol) estimation: a potential biomarker of antioxidant status evaluation on heavy metal toxicities. Recent Patents on Biomarkers. 2013;3:36–43. doi: 10.2174/2210309011303010036. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical