Glypicans as Cancer Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 30352677
- PMCID: PMC6209326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.09.004
Glypicans as Cancer Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
Glypicans are a group of cell-surface glycoproteins in which heparan sulfate (HS) glycosaminoglycan chains are covalently linked to a protein core. The glypican gene family is broadly conserved across animal species and plays important roles in biological processes. Glypicans can function as coreceptors for multiple signaling molecules known for regulating cell growth, motility, and differentiation. Some members of the glypican family, including glypican 2 (GPC2) and glypican 3 (GPC3), are expressed in childhood cancers and liver cancers, respectively. Antibody-based therapies targeting glypicans are being investigated in preclinical and clinical studies, with the goal of treating solid tumors that do not respond to standard therapies. These studies may establish glypicans as a new class of therapeutic targets for treating cancer.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; antibody-based therapy; childhood cancer; glypican; liver cancer.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) holds patent rights to anti-GPC2 and anti-GPC3 antibodies in many jurisdictions, including the United States [e.g., U.S. Patent 9,409,994, U.S. Patent 9,206,257, U.S Patent 9,304,364, U.S. Patent 9,932,406, U.S. Patent Application 62/716,169, and U.S. Patent Application 62/369,861], China, Japan, South Korea, Singapore and Europe. Claims cover the antibodies themselves, as well as conjugates that utilize the antibodies, such as recombinant immunotoxins (RITs), antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies and modified T cell receptors (TCRs)/chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), and vectors expressing these constructs. Anyone interested in licensing these antibodies can contact Dr. Mitchell Ho for additional information.
Figures

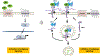



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

