Evolutionarily conserved Tbx5- Wnt2/2b pathway orchestrates cardiopulmonary development
- PMID: 30352852
- PMCID: PMC6233116
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1811624115
Evolutionarily conserved Tbx5- Wnt2/2b pathway orchestrates cardiopulmonary development
Abstract
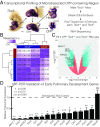
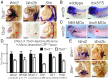
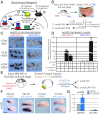
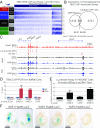
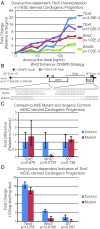
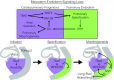
Codevelopment of the lungs and heart underlies key evolutionary innovations in the transition to terrestrial life. Cardiac specializations that support pulmonary circulation, including the atrial septum, are generated by second heart field (SHF) cardiopulmonary progenitors (CPPs). It has been presumed that transcription factors required in the SHF for cardiac septation, e.g., Tbx5, directly drive a cardiac morphogenesis gene-regulatory network. Here, we report instead that TBX5 directly drives Wnt ligands to initiate a bidirectional signaling loop between cardiopulmonary mesoderm and the foregut endoderm for endodermal pulmonary specification and, subsequently, atrial septation. We show that Tbx5 is required for pulmonary specification in mice and amphibians but not for swim bladder development in zebrafish. TBX5 is non-cell-autonomously required for pulmonary endoderm specification by directly driving Wnt2 and Wnt2b expression in cardiopulmonary mesoderm. TBX5 ChIP-sequencing identified cis-regulatory elements at Wnt2 sufficient for endogenous Wnt2 expression domains in vivo and required for Wnt2 expression in precardiac mesoderm in vitro. Tbx5 cooperated with Shh signaling to drive Wnt2b expression for lung morphogenesis. Tbx5 haploinsufficiency in mice, a model of Holt-Oram syndrome, caused a quantitative decrement of mesodermal-to-endodermal Wnt signaling and subsequent endodermal-to-mesodermal Shh signaling required for cardiac morphogenesis. Thus, Tbx5 initiates a mesoderm-endoderm-mesoderm signaling loop in lunged vertebrates that provides a molecular basis for the coevolution of pulmonary and cardiac structures required for terrestrial life.
Keywords: Hedgehog signaling; TBX5; Wnt signaling; heart development; lung development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Farmer CG. Evolution of the vertebrate cardio-pulmonary system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:573–592. - PubMed
-
- Jensen B, Spicer DE, Sheppard MN, Anderson RH. Development of the atrial septum in relation to postnatal anatomy and interatrial communications. Heart. 2017;103:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Jensen B, Wang T, Christoffels VM, Moorman AF. Evolution and development of the building plan of the vertebrate heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1833:783–794. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL114898/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG054770/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD093363/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD072598/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007197/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD084409/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL124836/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 LM012619/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070858/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018495/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007381/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD055164/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092153/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007281/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AG054770/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100407/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD089275/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007183/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010997/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

