Emergence of Morganella morganii subsp. morganii in dairy calves, China
- PMID: 30353002
- PMCID: PMC6199266
- DOI: 10.1038/s41426-018-0173-3
Emergence of Morganella morganii subsp. morganii in dairy calves, China
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
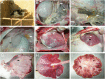
Figures
References
-
- Lee IK, Liu JW. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality in Morganella morganii bacteremia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2006;39:328–334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
