Increased CD74 binding and EAE treatment efficacy of a modified DRα1 molecular construct
- PMID: 30353480
- PMCID: PMC6364671
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-018-0331-2
Increased CD74 binding and EAE treatment efficacy of a modified DRα1 molecular construct
Abstract
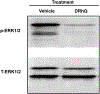
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating and degenerative disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with a strong inflammatory component that affects more than 2 million people worldwide (and at least 400,000 in the United States). In MS, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT) enhance the inflammatory event as a result of their interaction with their cognate receptor CD74. Therefore, the search for new agents aimed at blocking this interaction is critical for therapeutic purposes and will be of paramount importance for the treatment of MS. DRα1-MOG-35-55 constructs have been demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) a mouse model for MS. This effect is directly correlated with the binding to its cell surface receptor, CD74, apparently preventing or blocking the binding of two inflammatory factors, MIF and D-DT. Here we report that a single amino acid substitution (L50Q) in the DRα1 domain of the human and mouse DRα1-MOG-35-55 constructs (notated as DRhQ and DRmQ, respectively) possessed increased affinity for CD74, a greater capacity to block MIF binding, the ability to inhibit pERK1/2 signaling and increased therapeutic activity in mice with EAE. These data suggest that binding affinity for CD74 could serve as an in vitro indicator of biological potency of DRhQ and thus support its possible clinical utility as an effective therapy for MS and perhaps other diseases in which there is an inflammatory reaction driven by MIF and D-DT.
Keywords: CD74; D-dopachrome tautomerase; EAE; MIF; Multiple sclerosis; pERK1/2.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


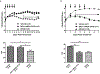
References
-
- Benedek G, Meza-Romero R, Jordan K, Keenlyside L, Offner H, Vandenbark AA (2015) HLA-DRalpha1-mMOG-35-55 treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis reduces CNS inflammation, enhances M2 macrophage frequency, and promotes neuroprotection J Neuroinflammation 12:123 doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0342-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

