Conophylline suppresses pancreatic cancer desmoplasia and cancer-promoting cytokines produced by cancer-associated fibroblasts
- PMID: 30353606
- PMCID: PMC6317962
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13847
Conophylline suppresses pancreatic cancer desmoplasia and cancer-promoting cytokines produced by cancer-associated fibroblasts
Abstract
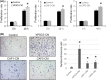
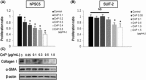
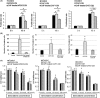
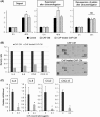
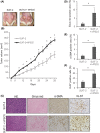
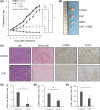
Despite recent advances in cancer treatment, pancreatic cancer is a highly malignant tumor type with a dismal prognosis and it is characterized by dense desmoplasia in the cancer tissue. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are responsible for this fibrotic stroma and promote cancer progression. We previously reported that a novel natural compound conophylline (CnP) extracted from the leaves of a tropical plant reduced liver and pancreatic fibrosis by suppression of stellate cells. However, there have been no studies to investigate the effects of CnP on CAF, which is the aim of this work. Here, we showed that CAF stimulated indicators of pancreatic cancer malignancy, such as proliferation, invasiveness, and chemoresistance. We also showed that CnP suppressed CAF activity and proliferation, and inhibited the stimulating effects of CAF on pancreatic cancer cells. Moreover, CnP strongly decreased the various cytokines involved in cancer progression, such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), secreted by CAF. In vivo, CAF promoted tumor proliferation and desmoplastic formation in a mouse xenograft model, CnP reduced desmoplasia of tumors composed of pancreatic cancer cells + CAF, and combination therapy of CnP with gemcitabine remarkably inhibited tumor proliferation. Our findings suggest that CnP is a promising therapeutic strategy of combination therapy with anticancer drugs to overcome refractory pancreatic cancers.
Keywords: conophylline; cytokine; fibroblast; microenvironment; stellate cell.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

