Increased Expression of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 5B (KDM5B) Promotes Tumor Cell Growth in Hep3B Cells and is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 30353907
- PMCID: PMC6210936
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.910844
Increased Expression of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 5B (KDM5B) Promotes Tumor Cell Growth in Hep3B Cells and is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
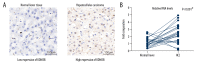
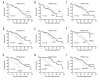
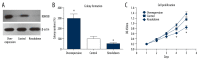
BACKGROUND Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) is overexpressed in several types of cancer. However, the clinical significance of KDM5B expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. The aims of the present study were to examine the functional effects of KDM5B in the Hep3B cell line, the expression levels of KDM5B in human HCC tissues, and the association between KDM5B expression and clinical outcome in patients with HCC. MATERIAL AND METHODS Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were used to examine the expression levels of KDM5B in HCC tissues and adjacent normal liver tissues. In the HCC cell line, Hep3B, the effects of KDM5B on cell proliferation and migration, and KDM5B small interfering RNA (siRNA) were used to study KDM5B knockdown. Univariate and multivariate analysis assessed the prognostic role of KDM5B in HCC patients. Kaplan-Meier analysis and the log-rank test evaluated clinical outcomes. RESULTS In the HCC cell line, Hep3B, KDM5B expression promoted promote tumor cell proliferation and colony formation. Increased expression of KDM5B in HCC tissues, compared with adjacent normal liver tissues, and was associated with larger tumor size, advanced TNM stage, and reduced overall survival in patients with HCC. Multivariate analysis identified KDM5B expression as an independent prognostic factor. CONCLUSIONS Increased expression of KDM5B was significantly correlated with poorer prognosis in patients with patients with HCC, indicating the possible potential of KDM5B as a novel clinical biomarker and therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depletion of histone demethylase KDM5B inhibits cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulation of cell cycle checkpoint proteins p15 and p27.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 25;35:37. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0311-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26911146 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein induces hepatic stem cell-like features in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating KDM5B.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 May 14;23(18):3252-3261. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3252. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28566884 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the hypoxia-related gene, JMJD1A, in hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical impact on recurrence after hepatic resection.Ann Surg Oncol. 2012 Jul;19 Suppl 3:S355-64. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-1797-x. Epub 2011 May 24. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21607773
-
KDM5B regulates the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway to increase sorafenib-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Oct 1;33(9):840-849. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001329. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35946516
-
Histone demethylase lysine demethylase 5B in development and cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8980-8991. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13858. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27974677 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylated KIAA1429 by TIP60 facilitates metastasis and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via N6-methyladenosine-KDM5B-mediated regulation of FoxO1.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 29;11(1):210. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02462-4. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40301310 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of AKR1B10 as a key gene in primary biliary cholangitis by integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 9;10:1124956. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1124956. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36845547 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HOXC-AS3 accelerates malignant proliferation of cervical cancer cells via stabilizing KDM5B.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 6;150(6):294. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05799-y. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38842683 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, Prognostic Value, and Functional Mechanism of the KDM5 Family in Pancreatic Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 13;10:887385. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.887385. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35493099 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2023 May 20;4(3):e292. doi: 10.1002/mco2.292. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37220590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mortezaee K. Human hepatocellular carcinoma: Protection by melatonin. J Cell Physiol. 2018 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

