Human Urinary mRNA as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 30354328
- PMCID: PMC6760265
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.118.002213
Human Urinary mRNA as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
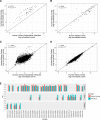
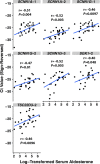
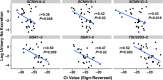
Background mRNA in urine supernatant (US-mRNA) might encode information about renal and cardiorenal pathophysiology, including hypertension. H, whether the US-mRNA transcriptome reflects that of renal tissues and whether changes in renal physiology are detectable using US-mRNA is unknown. Methods We compared transcriptomes of human urinary extracellular vesicles and human renal cortex. To avoid similarities attributable to ubiquitously expressed genes, we separately analyzed ubiquitously expressed and highly kidney-enriched genes. To determine whether US-mRNA reflects changes in renal gene expression, we assayed cell-depleted urine for transcription factor activity of mineralocorticoid receptors (MR) using probe-based quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The urine was collected from prehypertensive individuals (n=18) after 4 days on low-sodium diet to stimulate MR activity and again after suppression of MR activity via sodium infusion. Results In comparing this US-mRNA and human kidney cortex, expression of 55 highly kidney-enriched genes correlated strongly (rs=0.82) while 8457 ubiquitously expressed genes correlated moderately (rs=0.63). Standard renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system phenotyping confirmed the expected response to sodium loading. Cycle threshold values for MR-regulated targets ( SCNN1A, SCNN1G, TSC22D3) changed after sodium loading, and MR-regulated targets ( SCNN1A, SCNN1G, SGK1, and TSC22D3) correlated significantly with serum aldosterone and inversely with urinary sodium excretion. Conclusions RNA-sequencing of urinary extracellular vesicles shows concordance with human kidney. Perturbation in human endocrine signaling (MR activation) was accompanied by changes in mRNA in urine supernatant. Our findings could be useful for individualizing pharmacological therapy in patients with disorders of mineralocorticoid signaling, such as resistant hypertension. More generally, these insights could be used to noninvasively identify putative biomarkers of disordered renal and cardiorenal physiology.
Keywords: RNA, messenger; blood pressure; kidney; mineralocorticoids; urine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ENaCγ in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles as an Indicator of MR Signaling in Primary Aldosteronism.Hypertension. 2024 Dec;81(12):2457-2467. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.23379. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Hypertension. 2024. PMID: 39319458 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of mineralocorticoid effector mechanisms in kidney biopsies of patients with heavy proteinuria.Circulation. 2005 Sep 6;112(10):1435-43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.539122. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 16145013
-
Aberrant Rac1-mineralocorticoid receptor pathways in salt-sensitive hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013 Dec;40(12):929-36. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12177. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24111570 Review.
-
Inducible Knock-Down of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor in Mice Disturbs Regulation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Attenuates Heart Failure Induced by Pressure Overload.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 25;10(11):e0143954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143954. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26605921 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs and the mineralocorticoid receptor in the kidney.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Feb 5;521:111115. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.111115. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33301840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Medicine and the future of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Clinically Oriented Comprehensive Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 23;12(5):1799. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051799. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capturing the Kidney Transcriptome by Urinary Extracellular Vesicles-From Pre-Analytical Obstacles to Biomarker Research.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 8;14(7):1415. doi: 10.3390/genes14071415. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510317 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics Analysis of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2668:57-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3203-1_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37140790
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles carry valuable hints through mRNA for the understanding of endocrine hypertension.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 29;14:1155011. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1155011. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37065732 Free PMC article.
-
From salt to hypertension, what is missed?J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021 Dec;23(12):2033-2041. doi: 10.1111/jch.14402. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021. PMID: 34846798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

