Renal Medullary Interstitial COX-2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) Is Essential in Preventing Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Maintaining Renal Inner Medulla/Papilla Structural Integrity
- PMID: 30354807
- PMCID: PMC6207229
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11694
Renal Medullary Interstitial COX-2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) Is Essential in Preventing Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Maintaining Renal Inner Medulla/Papilla Structural Integrity
Abstract
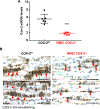
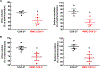
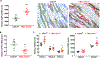
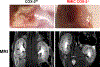
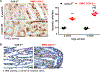
COX (cyclooxygenase)-derived prostaglandins regulate renal hemodynamics and salt and water homeostasis. Inhibition of COX activity causes blood pressure elevation. In addition, chronic analgesic abuse can induce renal injury, including papillary necrosis. COX-2 is highly expressed in the kidney papilla in renal medullary interstitial cells (RMICs). However, its role in blood pressure and papillary integrity in vivo has not been definitively studied. In mice with selective, inducible RMIC COX-2 deletion, a high-salt diet led to an increase in blood pressure that peaked at 4 to 5 weeks and was associated with increased papillary expression of AQP2 (aquaporin 2) and ENac (epithelial sodium channel) and decreased expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. With continued high-salt feeding, the mice with RMIC COX-2 deletion had progressive decreases in blood pressure from its peak. After return to a normal-salt diet for 3 weeks, blood pressure remained low and was associated with a persistent urinary concentrating defect. Within 2 weeks of institution of a high-salt diet, increased apoptotic RMICs and collecting duct cells could be detected in papillae with RMIC deletion of COX-2, and by 9 weeks of high salt, there was a striking loss of the papillae. Therefore, RMIC COX-2 expression plays a crucial role in renal handling water and sodium homeostasis, preventing salt-sensitive hypertension and maintaining structural integrity of papilla.
Keywords: blood pressure; homeostasis; kidney; mice; prostaglandin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and function of COX isoforms in renal medulla: evidence for regulation of salt sensitivity and blood pressure.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F542-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00232.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16189289
-
Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostacyclin formation and blood pressure homeostasis: targeted exchange of cyclooxygenase isoforms in mice.Circ Res. 2010 Feb 5;106(2):337-45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.204529. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 19940265 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a tenascin-C-CreER2 knockin mouse line for conditional DNA recombination in renal medullary interstitial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e79839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079839. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244568 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of renal medullary cyclooxygenase-2 during high salt loading.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017 Jan 1;22(1):128-136. doi: 10.2741/4476. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017. PMID: 27814606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The renal medullary endothelin system in control of sodium and water excretion and systemic blood pressure.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2006 Jan;15(1):34-40. doi: 10.1097/01.mnh.0000186852.15889.1a. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2006. PMID: 16340664 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal interstitial cells promote nephron regeneration by secreting prostaglandin E2.Elife. 2023 Jan 16;12:e81438. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81438. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36645741 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine Causes Endothelial Dysfunction via Inflammatory Factor-Mediated Activation of Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC).Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 17;9:672335. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.672335. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34222246 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Staining of CD8α in Diabetic Mouse Kidney.Bio Protoc. 2019 Sep 20;9(18):e3364. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3364. eCollection 2019 Sep 20. Bio Protoc. 2019. PMID: 33654861 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Prostaglandin E2 Excretion and the Risk of Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Feb 20;13(4):e032835. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032835. Epub 2024 Feb 16. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38362883 Free PMC article.
-
Permanent defects in renal medullary structure and function after reversal of urinary obstruction.JCI Insight. 2025 Jan 23;10(5):e187008. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.187008. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39847447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris RC. Cyclooxygenase-2 in rat nephron development. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:F994–1002. - PubMed
-
- Harris RC. Cox-2 and the kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2006;47 Suppl 1:S37–42. - PubMed
-
- Kohsaka S, Volcik KA, Folsom AR, Wu KK, Ballantyne CM, Willerson JT, Boerwinkle E. Increased risk of incident stroke associated with the cyclooxygenase 2 (cox-2) g-765c polymorphism in african-americans: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Atherosclerosis. 2008;196:926–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

