Attenuation of Microbiotal Dysbiosis and Hypertension in a CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Ablation Rat Model of GPER1
- PMID: 30354811
- PMCID: PMC6208154
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11175
Attenuation of Microbiotal Dysbiosis and Hypertension in a CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Ablation Rat Model of GPER1
Abstract
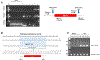
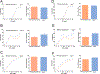
G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor, Gper1, has been implicated in cardiovascular disease, but its mechanistic role in blood pressure control is poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that genetically salt-sensitive hypertensive rats with complete genomic excision of Gper1 by a multiplexed guide RNA CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)/Cas9 (CRISPR associated proteins) approach present with lower blood pressure, which was accompanied by altered microbiota, different levels of circulating short chain fatty acids, and improved vascular relaxation. Microbiotal transplantation from hypertensive Gper1+/+ rats reversed the cardiovascular protective effect exerted by the genomic deletion of Gper1. Thus, this study reveals a role for Gper1 in promoting microbiotal alterations that contribute to cardiovascular pathology. However, the exact mechanism by which Gper1 regulates blood pressure is still unknown. Our results indicate that the function of Gper1 is contextually dependent on the microbiome, whereby, contemplation of using Gper1 as a target for therapy of cardiovascular disease requires caution.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas systems; blood pressure; genomics; hypertension; microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
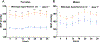
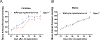
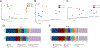
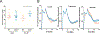
Comment in
-
Permissive Role of GPER for Arterial Hypertension.Hypertension. 2019 Feb;73(2):e9-e10. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12159. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 30595124 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Salt-Responsive Gut Microbiota Induces Sex-Specific Blood Pressure Changes.Circ Res. 2024 Dec 6;135(12):1122-1137. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325056. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 39440438
-
Gestational gut microbial remodeling is impaired in a rat model of preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension.Physiol Genomics. 2021 Mar 1;53(3):125-136. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00121.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Physiol Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33491590 Free PMC article.
-
SeqCor: correct the effect of guide RNA sequences in clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas9 screening by machine learning algorithm.J Genet Genomics. 2020 Nov 20;47(11):672-680. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2020.10.007. Epub 2020 Nov 28. J Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33451939
-
[Advances in application of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated 9 system in stem cells research].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 20;34(4):253-256. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.04.013. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29690746 Review. Chinese.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Guide RNA Design Rules for Predicting Activity.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2115:351-364. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0290-4_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32006410 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids: Implications for cardiovascular and metabolic disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 11;9:900381. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.900381. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36035928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis reveals novel key biomarkers and potential candidate small molecule drugs in gestational diabetes mellitus.Biosci Rep. 2021 May 28;41(5):BSR20210617. doi: 10.1042/BSR20210617. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33890634 Free PMC article.
-
Rat models of human diseases and related phenotypes: a systematic inventory of the causative genes.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Aug 2;27(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00673-8. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32741357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbial Metabolites and Blood Pressure Regulation: Focus on SCFAs and TMAO.Physiology (Bethesda). 2020 Jul 1;35(4):275-284. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00004.2020. Physiology (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32490748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 in Cardiovascular Medicine: Unlocking New Potential for Treatment.Cells. 2025 Jan 17;14(2):131. doi: 10.3390/cells14020131. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Le Poul E, Loison C, Struyf S, et al. Functional characterization of human receptors for short chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2003;278(28):25481–25489. - PubMed
-
- Takada Y, Kato C, Kondo S, Korenaga R, Ando J. Cloning of cDNAs encoding G protein-coupled receptor expressed in human endothelial cells exposed to fluid shear stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;240(3):737–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

