Taurine attenuates acrylamide-induced axonal and myelinated damage through the Akt/GSK3β-dependent pathway
- PMID: 30354842
- PMCID: PMC6202743
- DOI: 10.1177/2058738418805322
Taurine attenuates acrylamide-induced axonal and myelinated damage through the Akt/GSK3β-dependent pathway
Abstract
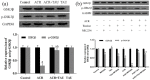
Acrylamide (ACR), formed during the Maillard reaction induced by high temperature in food processing, is one of the main causes of neurodegenerative diseases. Taurine, a free intracellular β-amino acid, is characterized by many functions, including antioxidation, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. This promotes its application in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. In this study, the neuroprotective effects of taurine against ACR-induced neurotoxicity and the potential underlying mechanisms were explored. Rats were intoxicated with ACR and injected with taurine in different groups for totally 2 weeks between January and July 2017. Electron microscopic analysis was used to observe the changes in tissues of the rats. Meanwhile, the levels of proteins including p-Akt, p-GSK3β, SIM312, and MBP were detected by Western blot. Furthermore, the GSK3β phosphorylation in taurine-treated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) with ACR was examined in the presence of the Akt inhibitor, MK-2206. The analysis of behavioral performances and electron micrographs indicated that taurine treatment significantly attenuated the toxic manifestations induced by ACR and stimulated the growth of axons and the medullary sheath, which was associated with the activation of the Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway. Mechanistically, it was found that taurine activated GSK3β, leading to significant recovery of the damage in ACR-induced sciatic nerves. Furthermore, MK-2206, an inhibitor of Akt, was applied in DRG cells, suggesting that taurine-induced GSK3β phosphorylation was Akt dependent. Our findings demonstrated that taurine attenuated ACR-induced neuropathy in vivo, in an Akt/GSK3β-dependent manner. This confirmed the treatment with taurine to be a novel strategy against ACR-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: Akt/GSK3β-dependent pathway; acrylamide; axonal and myelinated damage; taurine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Taurine protects against myelin damage of sciatic nerve in diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats by controlling apoptosis of schwann cells via NGF/Akt/GSK3β pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Oct 15;383(2):111557. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111557. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31415759
-
A hypothetic role of minocycline as a neuroprotective agent against methylphenidate-induced neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction and tau protein hyper-phosphorylation: Possible role of PI3/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway.Med Hypotheses. 2019 Jul;128:6-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.04.017. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Med Hypotheses. 2019. PMID: 31203911
-
Tau hyperphosphorylation and P-CREB reduction are involved in acrylamide-induced spatial memory impairment: Suppression by curcumin.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Jul;71:66-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.04.014. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 29704550
-
Acrylamide axonopathy revisited.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003 May 1;188(3):135-53. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(02)00072-8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12729714 Review.
-
Fast axonal transport: a site of acrylamide neurotoxicity?Neurotoxicology. 2002 Jul;23(2):223-51. doi: 10.1016/s0161-813x(02)00025-6. Neurotoxicology. 2002. PMID: 12224764 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of taurine against chemical and natural compound-induced toxicity: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04513-0. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40794180 Review.
-
Taurine ameliorates axonal damage in sciatic nerve of diabetic rats and high glucose exposed DRG neuron by PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent pathway.Amino Acids. 2021 Mar;53(3):395-406. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-02957-1. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33598769
-
CTRP6(C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-related protein-6) alleviated the sevoflurane induced injury of mice central nervous system by promoting the expression of p-Akt (phosphorylated Akt).Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5716-5726. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1967838. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34516328 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary acrylamide and physical performance tests: A cross-sectional analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 2;16(11):e0259320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259320. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34727127 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary acrylamide and incident osteoporotic fractures: an 8-year prospective cohort study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022 Oct;34(10):2441-2448. doi: 10.1007/s40520-022-02214-9. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022. PMID: 35962898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han JY, Zhang CW. (2006) Toxicity study for acrylamide. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 35: 513–515. - PubMed
-
- Parzefall W. (2008) Minireview on the toxicity of dietary acrylamide. Food and Chemical Toxicology 46: 1360–1364. - PubMed
-
- Tardiff RG, Gargas ML, Kirman RC, et al. (2010) Estimation of safe dietary intake levels of acrylamide for humans. Food and Chemical Toxicology 48: 658–667. - PubMed
-
- Haase NU, Grothe KH, Matthäus B, et al. (2012) Acrylamide formation and antioxidant level in biscuits related to recipe and baking. Food Additives and Contaminants. Part A, Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure and Risk Assess 29: 1230–1238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

