Pseudomonas aeruginosa LptE is crucial for LptD assembly, cell envelope integrity, antibiotic resistance and virulence
- PMID: 30354941
- PMCID: PMC7204523
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1537730
Pseudomonas aeruginosa LptE is crucial for LptD assembly, cell envelope integrity, antibiotic resistance and virulence
Abstract
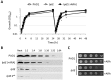
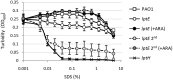
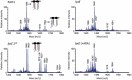
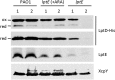
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an essential structural component of the outer membrane (OM) of most Gram-negative bacteria. In the model organism Escherichia coli, LPS transport to the OM requires seven essential proteins (LptABCDEFG) that form a continuous bridge across the cell envelope. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa the recently-demonstrated essentiality of LptD and LptH, the P. aeruginosa LptA homologue, confirmed the crucial role of the Lpt system and, thus, of LPS in OM biogenesis in this species. Surprisingly, independent high-throughput transposon mutagenesis studies identified viable P. aeruginosa insertion mutants in the lptE gene, suggesting that it might be dispensable for bacterial growth. To test this hypothesis, we generated an lptE conditional mutant in P. aeruginosa PAO1. LptE depletion only slightly impairs P. aeruginosa growth in vitro. Conversely, LptE is important for cell envelope stability, antibiotic resistance and virulence in an insect model. Interestingly, the maturation and OM localization of LPS is only marginally affected in LptE-depleted cells, while the levels of the OM component LptD are strongly reduced. This suggests that P. aeruginosa LptE might not be directly involved in LPS transport, although it is clearly essential for the maturation and/or stability of LptD. While poor functionality of LptD caused by LptE depletion is somehow tolerated by P. aeruginosa, this has a high cost in terms of cell integrity, drug resistance and virulence, highlighting LptE function(s) as an interesting target to weaken P. aeruginosa defenses and reduce its infectivity.
Keywords: Galleria mellonella; LPS transport; LptD; LptH; infection; lipid A; outer membrane; resistance; virulence.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide transport to the outer membrane in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by peptidomimetic antibiotics.Chembiochem. 2012 Aug 13;13(12):1767-75. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201200276. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Chembiochem. 2012. PMID: 22807320
-
Dominant negative lptE mutation that supports a role for LptE as a plug in the LptD barrel.J Bacteriol. 2013 Mar;195(6):1327-34. doi: 10.1128/JB.02142-12. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23316047 Free PMC article.
-
Solution Structure and Dynamics of LptE from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biochemistry. 2016 May 31;55(21):2936-43. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00313. Epub 2016 May 19. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27166502
-
Structural insight into lipopolysaccharide transport from the Gram-negative bacterial inner membrane to the outer membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Nov;1862(11):1461-1467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28821406 Review.
-
Structural Insights into the Lipopolysaccharide Transport (Lpt) System as a Novel Antibiotic Target.J Microbiol. 2024 Apr;62(4):261-275. doi: 10.1007/s12275-024-00137-w. Epub 2024 May 31. J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38816673 Review.
Cited by
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lipid A Structural Variants Induce Altered Immune Responses.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024 Aug;71(2):207-218. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0059OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38656811 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular comparison of [Fe-S] cluster-based homeostasis in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2024 Nov 13;15(11):e0120624. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01206-24. Epub 2024 Oct 3. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39360836 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetic Background and Culture Medium Only Marginally Affect the In Vitro Evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Toward Colistin Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;14(6):601. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14060601. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558191 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Genetic Approach to the Study of Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Galleria mellonella During Salmonella Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 1;11:640112. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.640112. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33732665 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Small Molecule That Inhibits the Interaction of LPS Transporters LptA and LptC.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;11(10):1385. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101385. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vollmer W, Blanot D, de Pedro MA. Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32:149–167. - PubMed
-
- Nikaido H. Restoring permeability barrier function to outer membrane. Chem Biol. 2005;12:507–509. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz N, Wu T, Khane D, et al. Probing the barrier function of the outer membrane with chemical conditionality. ACS Chem Biol. 2006;1:385–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
