Wall Shear Stress and T1 Contrast Ratio Are Associated With Embolic Signals During Carotid Exposure in Endarterectomy
- PMID: 30354998
- PMCID: PMC6116793
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022322
Wall Shear Stress and T1 Contrast Ratio Are Associated With Embolic Signals During Carotid Exposure in Endarterectomy
Abstract
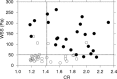
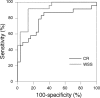
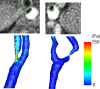
Background and Purpose- The frictional force because of blood flow may dislodge masses present on the surface of a plaque. Such frictional force is calculated as wall shear stress (WSS) using computational fluid dynamics. The aims of the present study were to determine whether, in addition to carotid plaque intensity on T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, WSS calculated using computational fluid dynamics analysis for carotid arteries is associated with development of an embolism during exposure of carotid arteries during carotid endarterectomy. Methods- One hundred patients with internal carotid artery stenosis (≥70%) underwent carotid plaque imaging with MR, and 54 patients with a vulnerable plaque (intraplaque hemorrhage or lipid/necrotic core) displayed as a high-intensity lesion underwent additional cervical 3-dimensional MR angiography. The maximum value of WSS within the most severe stenotic segment of the internal carotid artery was calculated using MR angiography. Transcranial Doppler monitoring of microembolic signals (MES) in the ipsilateral middle cerebral artery was performed during carotid endarterectomy. Results- Although none of the 46 patients with a nonvulnerable carotid plaque had MES during exposure of carotid arteries, 24 of the 54 patients with a vulnerable carotid plaque (44%) had MES. Logistic regression analysis showed that higher plaque intensity ( P=0.0107) and higher WSS ( P=0.0029) were significantly associated with the development of MES. When both cutoff points of plaque intensity and WSS in the receiver operating characteristic curves for predicting development of MES were combined, specificity (from 63% to 93%) and positive predictive value (from 66% to 90%) became greater than those for plaque intensity alone. Conclusions- In addition to carotid plaque intensity on T1-weighted MR imaging, WSS calculated using computational fluid dynamics analysis for carotid arteries is associated with development of an embolism during exposure of carotid arteries during carotid endarterectomy.
Keywords: angiography; carotid arteries; embolism; endarterectomy; magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response by Oshida et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Wall Shear Stress and T1 Contrast Ratio Are Associated With Embolic Signals During Carotid Exposure in Endarterectomy".Stroke. 2018 Dec;49(12):e342. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023441. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 30571447 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Steinman et al Regarding Article, "Wall Shear Stress and T1 Contrast Ratio Are Associated With Embolic Signals During Carotid Exposure in Endarterectomy".Stroke. 2018 Dec;49(12):e341. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023197. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 30571448 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Superb Microvascular Imaging Ultrasound for Cervical Carotid Artery Stenosis for Prediction of the Development of Microembolic Signals on Transcranial Doppler during Carotid Exposure in Endarterectomy.Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2021;11(2):61-68. doi: 10.1159/000516426. Epub 2021 May 25. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2021. PMID: 34034253 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative cervical carotid artery contrast-enhanced ultrasound findings are associated with development of microembolic signals on transcranial Doppler during carotid exposure in endarterectomy.Atherosclerosis. 2017 May;260:87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.03.026. Epub 2017 Mar 19. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28363131
-
Optimal MR Plaque Imaging for Cervical Carotid Artery Stenosis in Predicting the Development of Microembolic Signals during Exposure of Carotid Arteries in Endarterectomy: Comparison of 4 T1-Weighted Imaging Techniques.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Jun;37(6):1146-54. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4674. Epub 2016 Feb 4. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 26846926 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary carotid imaging: from degree of stenosis to plaque vulnerability.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):27-42. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26230478 Review.
-
Transcranial Doppler monitoring for microemboli: a marker of a high-risk carotid plaque.Semin Vasc Surg. 2017 Mar;30(1):62-66. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2017.04.011. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Semin Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28818260 Review.
Cited by
-
Hemodynamic Changes in the Carotid Artery after Infusion of Normal Saline Using Computational Fluid Dynamics.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Jul 12;10(7):473. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10070473. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32664658 Free PMC article.
-
Atherosclerotic plaque locations may be related to different ischemic lesion patterns.BMC Neurol. 2020 Jul 30;20(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-01868-0. BMC Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32731859 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Proximal Wall Shear Stress of Basilar Artery Plaques Associated with Ruptured Fibrous Cap.Brain Sci. 2022 Oct 17;12(10):1397. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12101397. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36291330 Free PMC article.
-
Complex carotid artery segmentation in multi-contrast MR sequences by improved optimal surface graph cuts based on flow line learning.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 Sep;60(9):2693-2706. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02622-z. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022. PMID: 35856128
-
Modern Concepts in Regenerative Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: From Stem Cells for Promoting Angiogenesis to 3D-Bioprinted Scaffolds Customized via Carotid Shear Stress Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 25;20(10):2574. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102574. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31130624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA, Fox AJ, Taylor DW, Mayberg MR, et al. Carotid Endarterectomy Trialists’ Collaboration. Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet. 2003;361:107–116. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12228-3. - PubMed
-
- Walker MD, Marler JR, Goldstein M, Grady PA, Toole JF, Baker WH, et al. Executive Committee for the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study. Endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. JAMA. 1995;273:1421–1428. doi: 10.1001/jama.1995.03520420037035. - PubMed
-
- Barnett HJM, Taylor DW, Haynes RB, Sackett DL, Peerless SJ, Ferguson GG, et al. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:445–453. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250701. - PubMed
-
- Spencer MP. Transcranial Doppler monitoring and causes of stroke from carotid endarterectomy. Stroke. 1997;28:685–691. - PubMed
-
- Ackerstaff RG, Moons KG, van de Vlasakker CJ, Moll FL, Vermeulen FE, Algra A, et al. Association of intraoperative transcranial doppler monitoring variables with stroke from carotid endarterectomy. Stroke. 2000;31:1817–1823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

