Focal Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Induce Brain Injury Through α2δ-1-Bound NMDA Receptors
- PMID: 30355118
- PMCID: PMC6205748
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022330
Focal Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Induce Brain Injury Through α2δ-1-Bound NMDA Receptors
Abstract
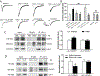
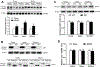
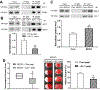
Background and Purpose- Glutamate NMDARs (N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors) play a major role in the initiation of ischemic brain damage. However, NMDAR antagonists have no protective effects in stroke patients, possibly because they impair physiological functions of NMDARs. α2δ-1 (encoded by Cacna2d1) is strongly expressed in many brain regions. We determined the contribution of α2δ-1 to NMDAR hyperactivity and brain injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. Methods- Mice were subjected to 90 minutes of middle cerebral artery occlusion followed by 24 hours of reperfusion. Neurological deficits, brain infarct volumes, and calpain/caspase-3 activity in brain tissues were measured. NMDAR activity of hippocampal CA1 neurons was measured in an in vitro ischemic model. Results- Middle cerebral artery occlusion increased α2δ-1 protein glycosylation in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and striatum. Coimmunoprecipitation showed that ischemia rapidly enhanced the α2δ-1-NMDAR physical interaction in the mouse brain tissue. Inhibiting α2δ-1 with gabapentin, uncoupling the α2δ-1-NMDAR interaction with an α2δ-1 C terminus-interfering peptide, or genetically ablating Cacna2d1 had no effect on basal NMDAR currents but strikingly abolished oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced NMDAR hyperactivity in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Systemic treatment with gabapentin or α2δ-1 C-terminus-interfering peptide or Cacna2d1 genetic knock-out reduced middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced infarct volumes, neurological deficit scores, and calpain/caspase-3 activation in brain tissues. Conclusions- α2δ-1 is essential for brain ischemia-induced neuronal NMDAR hyperactivity, and α2δ-1-bound NMDARs mediate brain damage caused by cerebral ischemia. Targeting α2δ-1-bound NMDARs, without impairing physiological α2δ-1-free NMDARs, may be a promising strategy for treating ischemic stroke.
Keywords: 3; NMDA receptor; brain; caspase; gabapentin; hippocampus; ischemia; neurons; pregabalin.
Figures



Similar articles
-
α2δ-1 Is Essential for Sympathetic Output and NMDA Receptor Activity Potentiated by Angiotensin II in the Hypothalamus.J Neurosci. 2018 Jul 11;38(28):6388-6398. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0447-18.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29921713 Free PMC article.
-
Brain α2δ-1-Bound NMDA Receptors Drive Calcineurin Inhibitor-Induced Hypertension.Circ Res. 2023 Sep 15;133(7):611-627. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322562. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37605933 Free PMC article.
-
The α2δ-1-NMDA receptor coupling is essential for corticostriatal long-term potentiation and is involved in learning and memory.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 14;293(50):19354-19364. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003977. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30355732 Free PMC article.
-
The α2δ-1-NMDA receptor complex and its potential as a therapeutic target for ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1148697. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1148697. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37153659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approach to the role of NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13(4):567-73. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660196. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24168367 Review.
Cited by
-
LRRC8A-dependent volume-regulated anion channels contribute to ischemia-induced brain injury and glutamatergic input to hippocampal neurons.Exp Neurol. 2020 Oct;332:113391. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113391. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32598930 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial calcium cycling in neuronal function and neurodegeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 24;11:1094356. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1094356. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36760367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcineurin regulates synaptic Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in hypothalamic presympathetic neurons via α2δ-1-mediated GluA1/GluA2 assembly.J Physiol. 2024 May;602(10):2179-2197. doi: 10.1113/JP286081. Epub 2024 Apr 17. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38630836 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia-reperfusion injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jan 8;9(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01688-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38185705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for α2δ subunits in calcium channel function and synaptic connectivity.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2020 Aug;63:162-169. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2020.04.007. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32521436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rossi DJ, Oshima T and Attwell D. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 2000;403:316–21. - PubMed
-
- Simon RP, Swan JH, Griffiths T and Meldrum BS. Blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors may protect against ischemic damage in the brain. Science 1984;226:850–2. - PubMed
-
- Lai TW, Shyu WC and Wang YT. Stroke intervention pathways: NMDA receptors and beyond. Trends Mol Med 2011;17:266–75. - PubMed
-
- Lipton SA. NMDA receptors, glial cells, and clinical medicine. Neuron 2006;50:9–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

