Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of tylosin against Streptococcus suis in pigs
- PMID: 30355326
- PMCID: PMC6201559
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-018-1645-3
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of tylosin against Streptococcus suis in pigs
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to optimize the dosage regimen of tylosin against S.suis in Pigs using pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modeling. The antibacterial activity of tylosin against S.suis CVCC606 was investigated in Mueller Hinton (MH) broth and serum. The objectives of this investigation were to study the PD data of tylosin against S.suis CVCC606 and the PK data of tylosin in healthy and diseased model of pigs and formulate a rational dosage regimen for the treatment of pig streptococcosis.
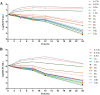
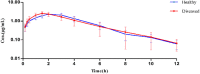
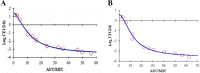
Results: The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were 0.25 μg/mL, and the minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBC) were 1 μg/mL in MH broth and serum. The killing curve showed time-dependent activity and weak concentration-dependent antibacterial activity. A pig pneumoniae model of S. suis infection was built by inoculating subcutaneously with S. suis CVCC606. Tylosin was (10 mg/kg b.w) administered intramuscularly (IM) to the healthy and S.suis infected pigs, The pharmacokinetic properties, including area under the curve(AUC), peak concentration (Cmax) and time to reach Cmax (Tmax), were determined in plasma using UV-HPLC method. The AUC, Cmax and Tmax in plasma of healthy and infected pigs were 10.80 ± 2.20 and 10.30 ± 3.46 μg.h/mL, 2.06 ± 0.43 and 2.37 ± 0.38 μg/mL, 1.95 ± 0.22 and 1.58 ± 0.49 h, respectively.
Conclusions: The in vivo PK and in vitro PD data were integrated to determine the surrogate marker of antibacterial activity, Cmax/MIC, AUC/MIC and T>MICwere 8.90, 43.21, 8.86 for healthy pigs, and 9.76, 41.18, 7.56 for infected pigs, respectively. Ex vivo AUC/MIC data were integrated with ex vivo bacterial count to calculate the values for bacteriostatic and bactericidal action, which were 10.67 h and 49.66 h for healthy pigs, 11.73 h and 43.03 h for pigs infected with S.suis. A dosage regimen of 5.32-19.50 mg/kg b.w. every 24 h should be sufficient for tylosin against S.suis.
Keywords: Dosage regimen; PK/PD modeling; Pig; Streptococcus suis; Tylosin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Huazhong Agricultural University and the Animal Care Center, Hubei Science and Technology Agency.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Seitz M, Valentin-Weigand P, Willenborg J. Use of antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance in veterinary medicine as exemplified by the swine pathogen Streptococcus suis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;398:103–121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

