INAVA-ARNO complexes bridge mucosal barrier function with inflammatory signaling
- PMID: 30355448
- PMCID: PMC6226287
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.38539
INAVA-ARNO complexes bridge mucosal barrier function with inflammatory signaling
Abstract
Homeostasis at mucosal surfaces requires cross-talk between the environment and barrier epithelial cells. Disruption of barrier function typifies mucosal disease. Here we elucidate a bifunctional role in coordinating this cross-talk for the inflammatory bowel disease risk-gene INAVA. Both activities require INAVA's DUF3338 domain (renamed CUPID). CUPID stably binds the cytohesin ARF-GEF ARNO to effect lateral membrane F-actin assembly underlying cell-cell junctions and barrier function. Unexpectedly, when bound to CUPID, ARNO affects F-actin dynamics in the absence of its canonical activity as a guanine nucleotide-exchange factor. Upon exposure to IL-1β, INAVA relocates to form cytosolic puncta, where CUPID amplifies TRAF6-dependent polyubiquitination and inflammatory signaling. In this case, ARNO binding to CUPID negatively-regulates polyubiquitination and the inflammatory response. INAVA and ARNO act similarly in primary human macrophages responding to IL-1β and to NOD2 agonists. Thus, INAVA-CUPID exhibits dual functions, coordinated directly by ARNO, that bridge epithelial barrier function with extracellular signals and inflammation.
Keywords: ARNO; IL-1b; TRAF6; actin assembly; biochemistry; cell biology; chemical biology; epithelial barrier; human; inflammatory bowel disease.
© 2018, Luong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PL, MH, JY, TZ, TF, JT, SH, CL, HW, CA, WL No competing interests declared, XJ is affiliated with Novartis. The author has no other competing interests to declare
Figures
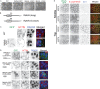
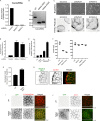
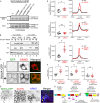
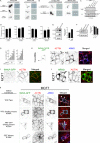

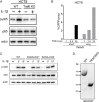

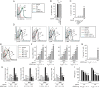
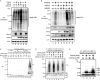
References
-
- Aksentijevich I, Masters SL, Ferguson PJ, Dancey P, Frenkel J, van Royen-Kerkhoff A, Laxer R, Tedgård U, Cowen EW, Pham TH, Booty M, Estes JD, Sandler NG, Plass N, Stone DL, Turner ML, Hill S, Butman JA, Schneider R, Babyn P, El-Shanti HI, Pope E, Barron K, Bing X, Laurence A, Lee CC, Chapelle D, Clarke GI, Ohson K, Nicholson M, Gadina M, Yang B, Korman BD, Gregersen PK, van Hagen PM, Hak AE, Huizing M, Rahman P, Douek DC, Remmers EF, Kastner DL, Goldbach-Mansky R. An autoinflammatory disease with deficiency of the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;360:2426–2437. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0807865. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashwood P, Harvey R, Verjee T, Wolstencroft R, Thompson RP, Powell JJ. Functional interactions between mucosal IL-1, IL-ra and TGF-beta 1 in ulcerative colitis. Inflammation Research : Official Journal of the European Histamine Research Society ... [Et Al.] 2004;53:53–59. doi: 10.1007/s00011-003-1219-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cappola TP, Li M, He J, Ky B, Gilmore J, Qu L, Keating B, Reilly M, Kim CE, Glessner J, Frackelton E, Hakonarson H, Syed F, Hindes A, Matkovich SJ, Cresci S, Dorn GW. Common variants in HSPB7 and FRMD4B associated with advanced heart failure. Circulation. Cardiovascular Genetics. 2010;3:147–154. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.898395. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK084424/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI124491/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099097/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK048106/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048106/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32HD007466/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK099097/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007466/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK048106/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK084424/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

