Hair follicle epidermal stem cells define a niche for tactile sensation
- PMID: 30355452
- PMCID: PMC6226291
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.38883
Hair follicle epidermal stem cells define a niche for tactile sensation
Abstract
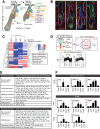
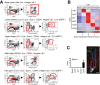
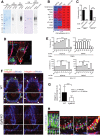
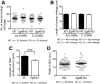
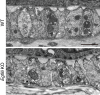
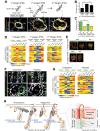
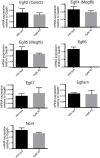
The heterogeneity and compartmentalization of stem cells is a common principle in many epithelia, and is known to function in epithelial maintenance, but its other physiological roles remain elusive. Here we show transcriptional and anatomical contributions of compartmentalized epidermal stem cells in tactile sensory unit formation in the mouse hair follicle. Epidermal stem cells in the follicle upper-bulge, where mechanosensory lanceolate complexes innervate, express a unique set of extracellular matrix (ECM) and neurogenesis-related genes. These epidermal stem cells deposit an ECM protein called EGFL6 into the collar matrix, a novel ECM that tightly ensheathes lanceolate complexes. EGFL6 is required for the proper patterning, touch responses, and αv integrin-enrichment of lanceolate complexes. By maintaining a quiescent original epidermal stem cell niche, the old bulge, epidermal stem cells provide anatomically stable follicle-lanceolate complex interfaces, irrespective of the stage of follicle regeneration cycle. Thus, compartmentalized epidermal stem cells provide a niche linking the hair follicle and the nervous system throughout the hair cycle.
Keywords: developmental biology; extracellular matrix; hair follicle; mouse; regenerative medicine; skin; stem cell; stem cells; tactile sensation.
© 2018, Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CC, KT, TT, NS, AN, KK, SY, CT, SK, HK, YF, YT, FW, HF No competing interests declared
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

