Transcriptional Programming of Normal and Inflamed Human Epidermis at Single-Cell Resolution
- PMID: 30355494
- PMCID: PMC6367716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.006
Transcriptional Programming of Normal and Inflamed Human Epidermis at Single-Cell Resolution
Abstract
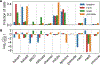
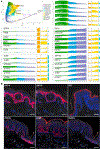
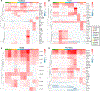
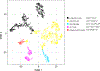
Perturbations in the transcriptional programs specifying epidermal differentiation cause diverse skin pathologies ranging from impaired barrier function to inflammatory skin disease. However, the global scope and organization of this complex cellular program remain undefined. Here we report single-cell RNA sequencing profiles of 92,889 human epidermal cells from 9 normal and 3 inflamed skin samples. Transcriptomics-derived keratinocyte subpopulations reflect classic epidermal strata but also sharply compartmentalize epithelial functions such as cell-cell communication, inflammation, and WNT pathway modulation. In keratinocytes, ∼12% of assessed transcript expression varies in coordinate patterns, revealing undescribed gene expression programs governing epidermal homeostasis. We also identify molecular fingerprints of inflammatory skin states, including S100 activation in the interfollicular epidermis of normal scalp, enrichment of a CD1C+CD301A+ myeloid dendritic cell population in psoriatic epidermis, and IL1βhiCCL3hiCD14+ monocyte-derived macrophages enriched in foreskin. This compendium of RNA profiles provides a critical step toward elucidating epidermal diseases of development, differentiation, and inflammation.
Keywords: epidermis; keratinocyte; single-cell RNA-seq; skin.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
More Than the Sum of Its Parts: Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals Epidermal Cell States.Cell Rep. 2018 Oct 23;25(4):823-824. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.041. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30355488
References
-
- Benoit S, Toksoy A, Ahlmann M, Schmidt M, Sunderko¨tter C, Foell D, Pasparakis M, Roth J, and Goebeler M (2006). Elevated serum levels of calcium-binding S100 proteins A8 and A9 reflect disease activity and abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol 155, 62–66. - PubMed
-
- Bolduc C, Sperling LC, and Shapiro J (2016). Primary cicatricial alopecia: Lymphocytic primary cicatricial alopecias, including chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, lichen planopilaris, frontal fibrosing alopecia, and Graham-Little syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol 75, 1081–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

