AKAP150 Palmitoylation Regulates Synaptic Incorporation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors to Control LTP
- PMID: 30355502
- PMCID: PMC6263960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.085
AKAP150 Palmitoylation Regulates Synaptic Incorporation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors to Control LTP
Abstract
Ca2+-permeable AMPA-type glutamate receptors (CP-AMPARs) containing GluA1 but lacking GluA2 subunits contribute to multiple forms of synaptic plasticity, including long-term potentiation (LTP), but mechanisms regulating CP-AMPARs are poorly understood. A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) 150 scaffolds kinases and phosphatases to regulate GluA1 phosphorylation and trafficking, and trafficking of AKAP150 itself is modulated by palmitoylation on two Cys residues. Here, we developed a palmitoylation-deficient knockin mouse to show that AKAP150 palmitoylation regulates CP-AMPAR incorporation at hippocampal synapses. Using biochemical, super-resolution imaging, and electrophysiological approaches, we found that palmitoylation promotes AKAP150 localization to recycling endosomes and the postsynaptic density (PSD) to limit CP-AMPAR basal synaptic incorporation. In addition, we found that AKAP150 palmitoylation is required for LTP induced by weaker stimulation that recruits CP-AMPARs to synapses but not stronger stimulation that recruits GluA2-containing AMPARs. Thus, AKAP150 palmitoylation controls its subcellular localization to maintain proper basal and activity-dependent regulation of synaptic AMPAR subunit composition.
Keywords: AKAP; LTD; LTP; PKA; PSD; calcineurin; calcium-permeable AMPA receptor; palmityolation.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

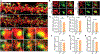
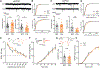



Similar articles
-
Control of Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity by AKAP-Anchored Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 14;38(11):2863-2876. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29440558 Free PMC article.
-
β-Amyloid disruption of LTP/LTD balance is mediated by AKAP150-anchored PKA and Calcineurin regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors.Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 5;37(1):109786. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109786. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34610314 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA Receptor-Dependent LTD Requires Transient Synaptic Incorporation of Ca²⁺-Permeable AMPARs Mediated by AKAP150-Anchored PKA and Calcineurin.Neuron. 2016 Mar 2;89(5):1000-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.043. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26938443 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
How Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors, the kinase PKA, and the phosphatase PP2B are intertwined in synaptic LTP and LTD.Sci Signal. 2016 Apr 26;9(425):e2. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf7067. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27117250 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Palmitoylation of Postsynaptic Proteins in Promoting Synaptic Plasticity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jan 31;12:8. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00008. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30766476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction and Subcellular Association of PRRT1/SynDIG4 With AMPA Receptors.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021 Aug 2;13:705664. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.705664. eCollection 2021. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34408636 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent post-translational regulation of palmitoylating and depalmitoylating enzymes in the hippocampus.J Cell Sci. 2023 Apr 1;136(7):jcs260629. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260629. Epub 2023 Apr 5. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37039765 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP150 and its Palmitoylation Contributed to Pain Hypersensitivity Via Facilitating Synaptic Incorporation of GluA1-Containing AMPA Receptor in Spinal Dorsal Horn.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Dec;58(12):6505-6519. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02570-z. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34559357
-
PKA-Dependent Membrane Surface Recruitment of CI-AMPARs Is Crucial for BCP-Mediated Protection Against Post-acute Ischemic Stroke Cognitive Impairment.Front Neurol. 2020 Dec 16;11:566067. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.566067. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33391143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beattie EC, Carroll RC, Yu X, Morishita W, Yasuda H, von Zastrow M, and Malenka RC (2000). Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nat. Neurosci 3, 1291–1300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

