The molecular and biochemical insight view of grape seed proanthocyanidins in ameliorating cadmium-induced testes-toxicity in rat model: implication of PI3K/Akt/Nrf-2 signaling
- PMID: 30355647
- PMCID: PMC6331675
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20180515
The molecular and biochemical insight view of grape seed proanthocyanidins in ameliorating cadmium-induced testes-toxicity in rat model: implication of PI3K/Akt/Nrf-2 signaling
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: The molecular and biochemical insight view of grape seed proanthocyanidins in ameliorating Cadmium-induced Testes-toxicity in rat model: Implication of PI3K/Akt/Nrf-2signaling.Biosci Rep. 2020 Aug 28;40(8):BSR-20180515_EOC. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20180515_EOC. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32749471 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
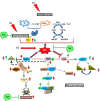
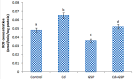
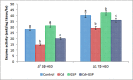
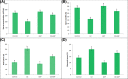
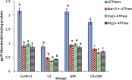
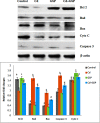
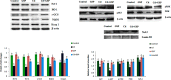
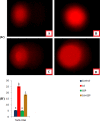
The present study aims to evaluate the protective effect of grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSP) on cadmium (Cd)-induced testicular apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in rats. A total of 24 male Wistar rats were divided into four groups, namely control, GSP (100 mg/kg BW), Cd (5 mg/kg BW), and Cd+GSP. Cd-treated rat testes exhibited a significant increment in oxidative stress mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Pre-administration of GSP exhibit significant protection against the apoptotic and inflammatory damages elicited by Cd and uphold the intercellular antioxidant status in testes. Histological changes were studied and the immunohistochemical staining for caspase 3, HSP70, and eNOS protein expressions were also analyzed to justify the protective action of GSP. Furthermore, GSP prevented DNA damage, and enhanced the expression of antioxidant responsive elements Nrf2/HO-1 by PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway. Therefore, our results suggest that GSP acts as a multipotent antioxidant entity against Cd-induced oxidative testicular toxicity in rats.
Keywords: Nrf2/HO-1; antioxidant; cadmium; grape seed proanthocyanidins; oxidative stress; testes.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
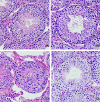
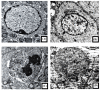
Similar articles
-
Grape seed proanthocyanidins ameliorates cadmium-induced renal injury and oxidative stress in experimental rats through the up-regulation of nuclear related factor 2 and antioxidant responsive elements.Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;93(3):210-26. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2014-0114. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. Retraction in: Biochem Cell Biol. 2020 Apr;98(2):307. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2020-0070. PMID: 25719599 Retracted.
-
Grape seed proanthocyanidins protects against cadmium induced oxidative pancreatitis in rats by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis via Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Jun;32:128-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27142746
-
Oxidative stress induced by cadmium in the plasma, erythrocytes and lymphocytes of rats: Attenuation by grape seed proanthocyanidins.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2016 Apr;35(4):428-47. doi: 10.1177/0960327115591376. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26089033
-
Potential protective roles of curcumin against cadmium-induced toxicity and oxidative stress.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2021 Apr 3;24(3):95-118. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2020.1860842. Epub 2020 Dec 23. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2021. PMID: 33357071 Review.
-
Revisiting cadmium-induced toxicity in the male reproductive system: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Nov;98(11):3619-3639. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03871-7. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39317800 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Steroidogenic Expression, Apoptotic, and Inflammatory Mediators in Polyphenol-Rich Extract of Ocimum gratissimum Mitigation of Cadmium-Induced Reprotoxicity in Male Rats.Vet Med Int. 2025 Jun 25;2025:9165137. doi: 10.1155/vmi/9165137. eCollection 2025. Vet Med Int. 2025. PMID: 40607242 Free PMC article.
-
[Luteolin has a significant protective effect against cadmium-induced injury in lung epithelial Beas-2B cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 May 20;41(5):729-735. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.05.14. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34134961 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Curative Potential of Substances with Bioactive Properties to Alleviate Cd Toxicity: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 28;19(19):12380. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912380. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutraceuticals: A New Challenge against Cadmium-Induced Testicular Injury.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 4;14(3):663. doi: 10.3390/nu14030663. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35277022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FTO Alleviates CdCl2-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via the AKT/Nrf2 Pathway in Bovine Granulosa Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4948. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094948. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsberg C.L. and Schwartze E.W. (1919) Pharmacological action of Cd. Pharmacology 13, 504–509
-
- Takiguchi M. and Yoshihara S. (2006) New aspects of cadmium as endocrine disruptor. Environ. Sci. 13, 107–116 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

