Comparative analysis of visual outcomes and ocular aberrations following wavefront optimized and topography-guided customized femtosecond laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and myopic astigmatism: A contralateral eye study
- PMID: 30355860
- PMCID: PMC6213678
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_507_18
Comparative analysis of visual outcomes and ocular aberrations following wavefront optimized and topography-guided customized femtosecond laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and myopic astigmatism: A contralateral eye study
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the visual outcomes and higher order aberrations (HOAs) following wavefront optimized (WFO) laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) versus topography-guided customized ablation (TCAT) LASIK for myopia and myopic astigmatism.
Methods: Patients who underwent femtosecond-assisted LASIK for myopic correction between August 2016 and October 2017 were included in this interventional prospective case series. The following parameters were evaluated preoperatively and at 3 months' postoperative visit: uncorrected distance vision acuity (UDVA) and corrected distance vision acuity (CDVA), manifest refraction, and HOAs.
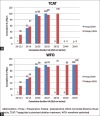
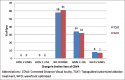
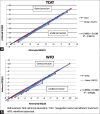
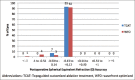
Results: Two hundred eyes of 100 patients were included in the study. At 3 months' postoperative visit, 92% and 90% eyes in the TCAT and WFO groups, respectively, demonstrated a UDVA of 20/20 or better (P = 0.90). A residual manifest spherical equivalent within 0.5 D was achieved in 100% and 95% of the eyes in the TCAT and WFO groups, respectively (P = 0.10). No significant difference was observed in the HOAs induced in both the groups, with slightly lower induction of trefoil and horizontal coma in the TCAT group.
Conclusion: Both groups demonstrated similar refractive efficacy and predictability, with greater gain of CDVA following TCAT ablation. HOAs induced were not significantly different between the two groups. Further studies are needed to validate the superiority of one procedure over the other.
Keywords: higher order aberrations; laser in situ keratomileusis; topography-guided customized ablation; wavefront optimized ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures
References
-
- Schallhorn SC, Farjo AA, Huang D, Wachler B, Trattler WB, Tanzer DJ, et al. Wavefront-guided LASIK for the correction of primary myopia and astigmatism a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1249–61. - PubMed
-
- El Awady HE, Ghanem AA, Saleh SM. Wavefront-optimized ablation versus topography-guided customized ablation in myopic LASIK: Comparative study of higher order aberrations. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2011;42:314–20. - PubMed
-
- Tan J, Simon D, Mrochen M, Por YM. Clinical results of topography-based customized ablations for myopia and myopic astigmatism. J Refract Surg. 2012;28:S829–S836. - PubMed
-
- Stulting D, Fant BS the T-CAT Study Group. Results of topography-guided laser in situ keratomileusis custom ablation treatment with refractive excimer laser. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016;42:11–8. - PubMed
-
- Sekundo W, Gertnere J, Bertelmann T, Solomatin I. One-year refractive results, contrast sensitivity, high-order aberrations and complications after myopic small-incision lenticule extraction (ReLEx SMILE) Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014;252:837–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

