Advanced Pharmaceutical Applications of Hot-Melt Extrusion Coupled with Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) 3D Printing for Personalised Drug Delivery
- PMID: 30356002
- PMCID: PMC6321644
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040203
Advanced Pharmaceutical Applications of Hot-Melt Extrusion Coupled with Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) 3D Printing for Personalised Drug Delivery
Abstract
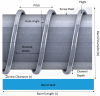
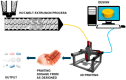
Three-dimensional printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a fabrication process whereby a 3D object is created layer-by-layer by depositing a feedstock material such as thermoplastic polymer. The 3D printing technology has been widely used for rapid prototyping and its interest as a fabrication method has grown significantly across many disciplines. The most common 3D printing technology is called the Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) which utilises thermoplastic filaments as a starting material, then extrudes the material in sequential layers above its melting temperature to create a 3D object. These filaments can be fabricated using the Hot-Melt Extrusion (HME) technology. The advantage of using HME to manufacture polymer filaments for FDM printing is that a homogenous solid dispersion of two or more pharmaceutical excipients i.e., polymers can be made and a thermostable drug can even be introduced in the filament composition, which is otherwise impractical with any other techniques. By introducing HME techniques for 3D printing filament development can improve the bioavailability and solubility of drugs as well as sustain the drug release for a prolonged period of time. The latter is of particular interest when medical implants are considered via 3D printing. In recent years, there has been increasing interest in implementing a continuous manufacturing method on pharmaceutical products development and manufacture, in order to ensure high quality and efficacy with less batch-to-batch variations of the pharmaceutical products. The HME and FDM technology can be combined into one integrated continuous processing platform. This article reviews the working principle of Hot Melt Extrusion and Fused Deposition Modelling, and how these two technologies can be combined for the use of advanced pharmaceutical applications.
Keywords: 3D printing; bioavailability; drug delivery; hot-melt extrusion; personalised medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Hoffman A.N. 3D Systems: “Stuck in The Middle” of the 3D Printer Boom? [(accessed on 18 June 2018)]; Available online: http://sk.sagepub.com/cases/3d-systems-stuck-in-the-middle-of-the-3d-pri....
-
- Manda V.R., Kampurath V., Msrk C. 3D Printing and its Effect on Outsourcing: A Study of the Indian Aircraft Industry. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2018;10 doi: 10.5028/jatm.v10.862. - DOI
-
- Tofail S.A.M., Koumoulos E.P., Bandyopadhyay A., Bose S., O’Donoghue L., Charitidis C. Additive manufacturing: Scientific and technological challenges, market uptake and opportunities. Mater. Today. 2018;21:22–37. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2017.07.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

