Quantification of ash sedimentation dynamics through depolarisation imaging with AshCam
- PMID: 30356119
- PMCID: PMC6200762
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34110-6
Quantification of ash sedimentation dynamics through depolarisation imaging with AshCam
Abstract
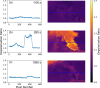
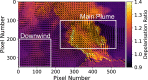
Even modest ash-rich volcanic eruptions can severely impact a range of human activities, especially air travel. The dispersal of ash in these eruptions depends critically on aggregation and sedimentation processes - however these are difficult to quantify in volcanic plumes. Here, we image ash dynamics from mild explosive activity at Santiaguito Volcano, Guatemala, by measuring the depolarisation of scattered sunlight by non-spherical ash particles, allowing the dynamics of diffuse ash plumes to be investigated with high temporal resolution (>1 Hz). We measure the ash settling velocity downwind from the main plume, and compare it directly with ground sampled ash particles, finding good agreement with a sedimentation model based on particle size. Our new, cost-effective technique leverages existing technology, opening a new frontier of integrated ash visualisation and ground collection studies which could test models of ash coagulation and sedimentation, leading to improved ash dispersion forecasts. This will provide risk managers with improved data quality on ash location, reducing the economic and societal impacts of future ash-rich eruptions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of particle volume fraction on the settling velocity of volcanic ash particles: insights from joint experimental and numerical simulations.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 3;7:39620. doi: 10.1038/srep39620. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28045056 Free PMC article.
-
A novel experimental chamber for the characterization of free-falling particles in volcanic plumes.Rev Sci Instrum. 2022 Jul 1;93(7):075105. doi: 10.1063/5.0093730. Rev Sci Instrum. 2022. PMID: 35922336
-
Hail formation triggers rapid ash aggregation in volcanic plumes.Nat Commun. 2015 Aug 3;6:7860. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8860. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26235052 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory health effects of volcanic ash with special reference to Iceland. A review.Clin Respir J. 2011 Jan;5(1):2-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-699X.2010.00231.x. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Clin Respir J. 2011. PMID: 21159135 Review.
-
[Effects of volcanic eruptions on human health in Iceland. Review].Laeknabladid. 2016 Oktober;102(10):433-441. doi: 10.17992/lbl.2016.10.101. Laeknabladid. 2016. PMID: 27813483 Review. Icelandic.
References
-
- Dingwell DB, Lavallée Y, Kueppers U. Volcanic ash: A primary agent in the Earth system. Phys. Chem. Earth. 2012;45-46:2–4. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2011.07.007. - DOI
-
- Horwell CJ, Baxter PJ. The respiratory health hazards of volcanic ash: A review for volcanic risk mitigation. Bull. Volcanol. 2006;69:1–24. doi: 10.1007/s00445-006-0052-y. - DOI
-
- Spence, R. J., Pomonis, A., Baxter, P. J., Coburn, A. W. & White, M. Building damage caused by the Mount Pinatubo eruption of June 15, 1991 In Fire and Mud: eruptions and lahars of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines. (eds Newall, C. G. & Punongbayan, R.) 1055–1061 (University of Washington Press, 1996).
-
- Bebbington M, Cronin SJ, Chapman I, Turner MB. Quantifying volcanic ash fall hazard to electricity infrastructure. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008;177:1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.07.023. - DOI
-
- Wilson TM, et al. Volcanic ash impacts on critical infrastructure. Phys. Chem. Earth. 2012;45–46:5–23. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2011.06.006. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

