Nanoparticles in Medicine: A Focus on Vascular Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 30356429
- PMCID: PMC6178176
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6231482
Nanoparticles in Medicine: A Focus on Vascular Oxidative Stress
Abstract
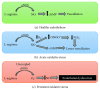
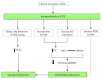
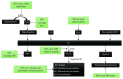
Nanotechnology has had a significant impact on medicine in recent years, its application being referred to as nanomedicine. Nanoparticles have certain properties with biomedical applications; however, in some situations, they have demonstrated cell toxicity, which has caused concern surrounding their clinical use. In this review, we focus on two aspects: first, we summarize the types of nanoparticles according to their chemical composition and the general characteristics of their use in medicine, and second, we review the applications of nanoparticles in vascular alteration, especially in endothelial dysfunction related to oxidative stress. This condition can lead to a reduction in nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, consequently affecting vascular tone regulation and endothelial dysfunction, which is the first phase in the development of cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, nanoparticles with antioxidant properties may improve vascular dysfunction associated with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or atherosclerosis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

