Effects of Tai Ji Quan training on gait kinematics in older Chinese women with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30356529
- PMCID: PMC6188600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jshs.2016.02.003
Effects of Tai Ji Quan training on gait kinematics in older Chinese women with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Although Tai Ji Quan has been shown to relieve pain and improve functional mobility in people with knee osteoarthritis (OA), little is known about its potential benefits on gait characteristics among older Chinese women who have a high prevalence of both radiographic and symptomatic knee OA. This study aims to assess the efficacy of a tailored Tai Ji Quan intervention on gait kinematics for older Chinese women with knee OA.
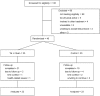
Methods: A randomized controlled trial involving 46 older women in Shanghai, China, with clinically diagnosed knee OA. Randomized (1:1) participants received either a 60 min Tai Ji Quan session (n = 23) 3 times weekly or a 60 min bi-weekly educational session (n = 23) for 24 weeks. Primary outcomes were changes in gait kinematic measures from baseline to 24 weeks. Secondary outcomes included changes in scores on the Western Ontario and McMaster University Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) and Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB).
Results: After 24 weeks the Tai Ji Quan group demonstrated better performance in gait velocity (mean difference, 8.40 cm/s, p = 0.01), step length (mean difference, 3.52 cm, p = 0.004), initial contact angle (mean difference, 2.19°, p = 0.01), and maximal angle (mean difference, 2.61°, p = 0.003) of flexed knees during stance phase compared to the control group. In addition, the Tai Ji Quan group showed significant improvement in WOMAC scores (p < 0.01) (mean difference, -4.22 points in pain, p = 0.002; -2.41 points in stiffness, p < 0.001; -11.04 points in physical function, p = 0.006) and SPPB scores (mean difference, 1.22 points, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Among older Chinese women with knee OA, a tailored Tai Ji Quan intervention improved gait outcomes. The intervention also improved overall function as indexed by the WOMAC and SPPB. These results support the use of Tai Ji Quan for older Chinese adults with knee OA to both improve their functional mobility and reduce pain symptomatology.
Keywords: Gait; Pain; Physical function; Rheumatic diseases; Tai Chi Quan.
References
-
- Zhang Y., Xu L., Nevitt M.C., Aliabadi P., Yu W., Qin M. Comparison of the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis between the elderly Chinese population in Beijing and whites in the United States: the Beijing osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2065–2071. - PubMed
-
- Felson D.T., Nevitt M.C., Zhang Y., Aliabadi P., Baumer B., Gale D. High prevalence of lateral knee osteoarthritis in Beijing Chinese compared with Framingham Caucasian subjects. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Jiang L., Rong J., Zhang Q., Hu F., Zhang S., Li X. Prevalence and associated factors of knee osteoarthritis in a community-based population in Heilongjiang, Northeast China. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32:1189–1195. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources