Ulinastatin May Significantly Improve Postoperative Cognitive Function of Elderly Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery by Reducing the Translocation of Lipopolysaccharide and Systemic Inflammation
- PMID: 30356711
- PMCID: PMC6189321
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01007
Ulinastatin May Significantly Improve Postoperative Cognitive Function of Elderly Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery by Reducing the Translocation of Lipopolysaccharide and Systemic Inflammation
Abstract
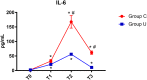
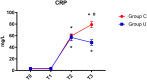
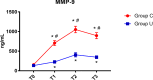
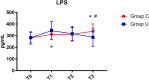
Background: Studies have shown that perioperative inflammatory response is one of the important factors that caused postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Ulinastatin is a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor that inhibits inflammatory. We investigated the effects of ulinastatin on inflammatory response and early postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery. Methods: This clinical trial was approved by the Xuanwu Hospital Ethical Committee (Registration number: ChiCTR-IPR-16008931). Sixty elderly patients undergoing elective spinal surgery with American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status of I-II were randomized into ulinastatin and control groups; total intravenous anesthesia was performed. The elderly patients in ulinastatin group underwent intravenous infusion of ulinastatin 10,000 units/kg following anesthesia induction and before surgical incision, and 5000 units/kg on post-operative days 1 and 2. Cognitive function was determined with Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) test preoperatively and on post-operative day 7 by a neurologist. Serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS), interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), and matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) concentration levels were measured at baseline, the end of surgery, and on post-operative days 1 and 3. Results: All elderly patients completed the study. Ulinastatin infusion significantly reduced the incidence of POCD in elderly patients undergoing spine surgery (ulinastatin group 16% vs. control group 43%, χ 2 = 5.079, P = 0.024, P < 0.05). The elderly patients in ulinastatin group exhibited lower serum LPS, IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 concentrations, as well as a shortened peak value duration, compared with those in the control group following surgery (P < 0.05). Conclusion: Systemic inflammation and translocation of LPS were inhibited by the infusion of ulinastatin in elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery. The anti-inflammation intervention with ulinastatin can significantly improve the elderly patients' postoperative cognitive function.
Keywords: POCD; elderly patients; lipopolysaccharide; spine surgery; systemic inflammation; ulinastatin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Ulinastatin on Early Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Elderly Patients Undergoing Surgery: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 21;15:618589. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.618589. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34248475 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ulinastatin Combined With Dexmedetomidine on Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients Who Underwent Cardiac Surgery.Front Neurol. 2019 Dec 19;10:1293. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01293. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31920917 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary study of the effects of ulinastatin on early postoperative cognition function in patients undergoing abdominal surgery.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Apr 29;541:15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23422155 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of ulinastatin on early postoperative cognitive function after one-lung ventilation surgery in elderly patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Apr;32(2):427-435. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9926-7. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 27830357 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Ulinastatin in the Treatment of Postperative Cognitive Dysfunction: Review of Current Literature.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2571080. doi: 10.1155/2016/2571080. Epub 2016 Aug 14. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27597957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preoperative cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers may be associated with postoperative delirium in patients undergoing knee/hip arthroplasty: the PNDABLE study.BMC Geriatr. 2023 May 10;23(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-03943-w. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37165310 Free PMC article.
-
Elamipretide (SS-31) Improves Functional Connectivity in Hippocampus and Other Related Regions Following Prolonged Neuroinflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Aged Rats.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Mar 1;13:600484. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.600484. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33732135 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome α-Synuclein Release in Plasma May be Associated With Postoperative Delirium in Hip Fracture Patients.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Mar 13;12:67. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00067. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32231560 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of combination of multiple anti-inflammatory drugs strategy on postoperative delirium among older patients undergoing hip fracture surgery: a pilot randomized controlled trial.BMC Med. 2025 Feb 21;23(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-03946-x. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 39985018 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Index of consciousness monitoring during general anesthesia may effectively enhance rehabilitation in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic urological surgery: a randomized controlled clinical trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Oct 4;23(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02300-z. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37794331 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

