Hyperglycemia Aggravates Diet-Induced Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial Infarction in SR-B1-Knockout/ApoE-Hypomorphic Mice
- PMID: 30356742
- PMCID: PMC6189369
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01398
Hyperglycemia Aggravates Diet-Induced Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial Infarction in SR-B1-Knockout/ApoE-Hypomorphic Mice
Abstract
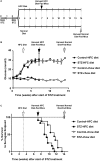
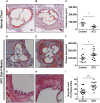
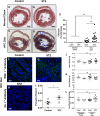
Diabetes is a risk factor for development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Animal model studies in mice revealed that hyperglycemia increases development of atherosclerosis in the aorta as well as myocardial fibrosis in surgical models of coronary artery ligation; however, the impact of hyperglycemia on coronary artery atherosclerosis and subsequent heart disease is less clear. To investigate the effect of hyperglycemia on atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease, we used a mouse model of diet-induced coronary artery atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction, the high fat/high cholesterol (HFC) diet fed SR-B1 knockout (KO)/apoE-hypomorphic (HypoE) mouse. Hyperglycemia was induced in these mice by streptozotocin (STZ) treatment. This increased HFC diet-dependent atherosclerosis development (p = 0.02) and necrotic core formation (p = 0.0008) in atherosclerotic plaques in the aortic sinus but did not increase the extent of atherosclerosis in coronary arteries. However, it did increase the extent of platelet accumulation in atherosclerotic coronary arteries (p = 0.017). This was accompanied by increased myocardial fibrosis (p = 0.005) and reduced survival (p = 0.01) compared to control-treated, normoglycemic mice. These results demonstrate that STZ-treatment exerted differential effects on the level of atherosclerosis in the aortic sinus and coronary arteries. These results also suggest that SR-B1-KO/HypoE mice may be a useful non-surgical model of diabetic cardiomyopathy in the context of coronary artery atherothrombosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; coronary artery; diabetes; fibrosis; hyperglycemia; myocardial infarction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SR-B1-/-ApoE-R61h/h Mice Mimic Human Coronary Heart Disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Dec;38(6):1123-1137. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07475-8. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 37273155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I knockout mice develop extensive diet-induced coronary artery atherosclerosis in an age-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2025 May 22;20(5):e0318118. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318118. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40403091 Free PMC article.
-
PAR4 Inhibition Reduces Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis and Myocardial Fibrosis in SR-B1/LDLR Double Knockout Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023 Nov;43(11):2165-2178. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.319767. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023. PMID: 37675637 Free PMC article.
-
SR-BI in bone marrow derived cells protects mice from diet induced coronary artery atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e72492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072492. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967310 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ezetimibe on atherosclerosis in preclinical models.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Apr;215(2):266-78. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.02.010. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21397230 Review.
Cited by
-
Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Is Associated With Augmented Lysosomal Signaling in Hypercholesterolemic Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Dec 3;13(23):e037460. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.037460. Epub 2024 Nov 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39604023 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha improves cardiac function in a novel diet-induced coronary atherosclerosis model, the SR-B1ΔCT/LDLR KO mouse.Atherosclerosis. 2024 Aug;395:117518. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2024.117518. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Atherosclerosis. 2024. PMID: 38627162 Free PMC article.
-
Brahma-Related Gene 1 Deficiency in Endothelial Cells Ameliorates Vascular Inflammatory Responses in Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 30;8:578790. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.578790. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33330454 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4/Midline-1 Axis Promotes T Lymphocyte Motility in Atherosclerosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Mar;10(9):e2204194. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204194. Epub 2023 Jan 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36683148 Free PMC article.
-
SR-B1-/-ApoE-R61h/h Mice Mimic Human Coronary Heart Disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Dec;38(6):1123-1137. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07475-8. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 37273155 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Braun A., Trigatti B. L., Post M. J., Sato K., Simons M., Edelberg J. M., et al. (2002). Loss of SR-BI expression leads to the early onset of occlusive atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, spontaneous myocardial infarctions, severe cardiac dysfunction, and premature death in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ. Res. 90 270–276. - PubMed
-
- Braun A., Zhang S., Miettinen H. E., Ebrahim S., Holm T. M., Vasile E., et al. (2003). Probucol prevents early coronary heart disease and death in the high-density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI/apolipoprotein E double knockout mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 7283–7288. 10.1073/pnas.1237725100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Ferranti S. D., de Boer I. H., Fonseca V., Fox C. S., Golden S. H., Lavie C. J., et al. (2014). Type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Circulation 130 1110–1130. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000034 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

