Dynamic and Functional Characteristics of Predominant Species in Industrial Paocai as Revealed by Combined DGGE and Metagenomic Sequencing
- PMID: 30356774
- PMCID: PMC6189446
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02416
Dynamic and Functional Characteristics of Predominant Species in Industrial Paocai as Revealed by Combined DGGE and Metagenomic Sequencing
Abstract
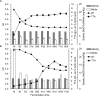
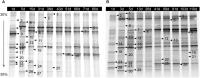
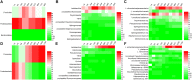
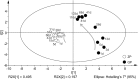
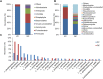
The microbial community during the fermentation of industrial paocai, a lactic acid fermented vegetable food, was investigated via combined denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and metagenomic sequencing. Firmicutes and Proteobacteria were identified as the dominant phyla during the fermentation. DGGE results of the bacterial community analysis showed that many genera were observed during the fermentation of industrial paocai, but the same predominant genus and species were observed: Lactobacillus and Lactobacillus (L.) alimentarius/L. paralimentarius. The abundance of L. alimentarius/L. paralimentarius increased fast during the initial stage of fermentation and approximately remained constant during the later stage. Metagenomic sequencing was used to finally identify the predominant species and their genetic functions. Metabolism was the primary functions of the microbial community in industrial paocai fermentation, including carbohydrate metabolism (CM), overview (OV), amino acid metabolism (AAM), nucleotide metabolism (NM), energy metabolism (EM), etc. The predominant species L. alimentarius and L. paralimentarius were involved in plenty of pathways in metabolism and played different roles in the metabolism of carbohydrate, amino acid, lipid to form flavor compounds during industrial paocai fermentation. This study provided valuable information about the predominant species in industrial paocai and its functional properties, which could enable us to advance our understanding of the fermentation mechanism during fermentation of industrial paocai. Our results will advance the understanding of the microbial roles in the industrial paocai fermentation and provide a theoretical basis for improving the quality of industrial paocai products.
Keywords: DGGE; dominant species; functional characteristics; industrial paocai; metagenomic sequencing.
Figures

References
-
- Bowman J. P. (2006). “The genus psychrobacter,” in The Prokaryotes, eds Dworkin M., Falkow S., E. Rosenberg, K. H. Schleifer, and E. Stackebrandt (New York, NY: Springer Press), 920–930.
-
- Cao J., Yang J., Hou Q., Xu H., Zheng Y., Zhang H., et al. (2017). Assessment of bacterial profiles in aged, home-made Sichuan paocai brine with varying titratable acidity by PacBio SMRT sequencing technology. Food Control 78 14–23. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.02.006 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

