Marginal-Zone B-Cells Are Main Producers of IgM in Humans, and Are Reduced in Patients With Autoimmune Vasculitis
- PMID: 30356862
- PMCID: PMC6190848
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02242
Marginal-Zone B-Cells Are Main Producers of IgM in Humans, and Are Reduced in Patients With Autoimmune Vasculitis
Abstract
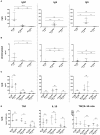
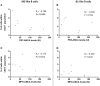
In mice, B1 and marginal zone (MZ) B-cells play an important role in prevention of autoimmunity through production of regulatory cytokines and natural antibodies. There is limited knowledge about the human counterparts of these cells. We therefore investigated functions of MZ-like B-cells and the frequency of circulating MZ-like and B1-like B-cells in healthy controls (HC), as well as in patients with autoimmune vasculitis to learn more about the role of these cells in autoimmune disease. After stimulation with CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN) of class B in vitro, MZ-like B-cells were the main producers of IgM whereas switched memory B-cells primarily produced IgG and IgA. TNF and IL-10 were produced by both MZ-like and switched memory B-cells. Neither antibody nor TNF/IL-10 production by the B-cell subsets differed between patients and HC. Patients with autoimmune vasculitis, irrespective of disease activity, had lower percentage and absolute numbers of circulating MZ-like B-cells, and lower absolute numbers of B1-like B-cells. The percentage of B1-like B-cells was reduced during active disease. These findings remained significant when the analysis was confined to active treatment-naïve patients (disease onset).Our results suggest that human innate-like B-cells might have a physiological role in prevention of autoimmunity.
Keywords: B1 B-cells; IgM; T-cell-independent antibodies; anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autantibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis; autoimmunity; innate-like B-cells; marginal-zone (MZ) B-cells; natural antibodies.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

