A Web Resource for Designing Subunit Vaccine Against Major Pathogenic Species of Bacteria
- PMID: 30356876
- PMCID: PMC6190870
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02280
A Web Resource for Designing Subunit Vaccine Against Major Pathogenic Species of Bacteria
Abstract
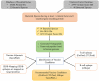
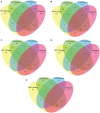
Evolution has led to the expansion of survival strategies in pathogens including bacteria and emergence of drug resistant strains proved to be a major global threat. Vaccination is a promising strategy to protect human population. Reverse vaccinology is a more robust vaccine development approach especially with the availability of large-scale sequencing data and rapidly dropping cost of the techniques for acquiring such data from various organisms. The present study implements an immunoinformatic approach for screening the possible antigenic proteins among various pathogenic bacteria to systemically arrive at epitope-based vaccine candidates against 14 pathogenic bacteria. Thousand four hundred and fifty nine virulence factors and Five hundred and forty six products of essential genes were appraised as target proteins to predict potential epitopes with potential to stimulate different arms of the immune system. To address the self-tolerance, self-epitopes were identified by mapping on 1000 human proteome and were removed. Our analysis revealed that 21proteins from 5 bacterial species were found as virulent as well as essential to their survival, proved to be most suitable vaccine target against these species. In addition to the prediction of MHC-II binders, B cell and T cell epitopes as well as adjuvants individually from proteins of all 14 bacterial species, a stringent criteria lead us to identify 252 unique epitopes, which are predicted to be T-cell epitopes, B-cell epitopes, MHC II binders and Vaccine Adjuvants. In order to provide service to scientific community, we developed a web server VacTarBac for designing of vaccines against above species of bacteria. This platform integrates a number of tools that includes visualization tools to present antigenicity/epitopes density on an antigenic sequence. These tools will help users to identify most promiscuous vaccine candidates in a pathogenic antigen. This server VacTarBac is available from URL (http://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/vactarbac/).
Keywords: antigen; epitopes; essential genes; immunotherapeutic; reverse vaccinology; vaccine designing; virulence factor.
Figures


References
-
- Neill JO'. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance Chaired (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

