Zinc-Modified Sulfonated Polyetheretherketone Surface with Immunomodulatory Function for Guiding Cell Fate and Bone Regeneration
- PMID: 30356934
- PMCID: PMC6193167
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201800749
Zinc-Modified Sulfonated Polyetheretherketone Surface with Immunomodulatory Function for Guiding Cell Fate and Bone Regeneration
Abstract
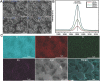
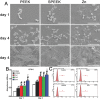
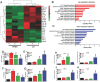
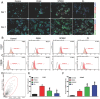
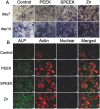
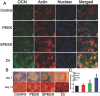
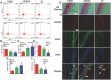
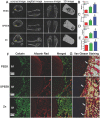
The cytokines released by immune cells are considered important factors to induce bone tissue regeneration. However, the pathway of those bone-targeting macrophage cytokines induced by biomaterial surface under tissue microenvironment is rarely reported. In this study, the immunomodulatory capability of zinc ions on macrophage polarization and its effects on osteogenic differentiation are investigated. Hence, a layer of zinc ions are incorporated on sulfonated polyetheretherketone (SPEEK) biomaterials by using a customized magnetron sputtering technique. The results reveal that the microenvironment on Zn-coated SPEEK can modulate nonactivated macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory phenotype and induce the secretion of anti-inflammatory and osteogenic cytokines. The osteogenic differentiation capability of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) is therefore enhanced, leading to improved osteointegration between the zinc-coated SPEEK and bone tissue. This study verifies that zinc ion is a promising additive in the osteoimmunomodulation process and provides knowledge that may pave the way to develop the next generation of immunomodulatory biomaterials.
Keywords: bone formation; immunomodulation; macrophages; stem cells; zinc.
Figures
References
-
- a) Chen Z., Klein T., Murray R. Z., Crawford R., Chang J., Wu C., Xiao Y., Mater. Today 2016, 19, 304;
- b) Takayanagi H., Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 292. - PubMed
-
- a) Takizawa T., Nakayama N., Haniu H., Aoki K., Okamoto M., Nomura H., Tanaka M., Sobajima A., Yoshida K., Kamanaka T., Ajima K., Oishi A., Kuroda C., Ishida H., Okano S., Kobayashi S., Kato H., Saito N., Adv. Mater. 2018, 30; - PubMed
- b) Pina S., Oliveira J. M., Reis R. L., Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1143. - PubMed
-
- Franz S., Rammelt S., Scharnweber D., Simon J. C., Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6692. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
