A Broad-Spectrum ROS-Eliminating Material for Prevention of Inflammation and Drug-Induced Organ Toxicity
- PMID: 30356945
- PMCID: PMC6193162
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201800781
A Broad-Spectrum ROS-Eliminating Material for Prevention of Inflammation and Drug-Induced Organ Toxicity
Abstract
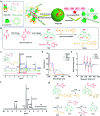
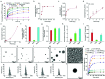
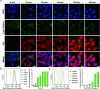
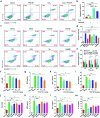
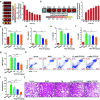
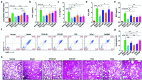
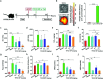
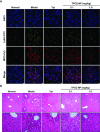
Despite the great potential of numerous antioxidants for pharmacotherapy of diseases associated with inflammation and oxidative stress, many challenges remain for their clinical translation. Herein, a superoxidase dismutase/catalase-mimetic material based on Tempol and phenylboronic acid pinacol ester simultaneously conjugated β-cyclodextrin (abbreviated as TPCD), which is capable of eliminating a broad spectrum of reactive oxygen species (ROS), is reported. TPCD can be easily synthesized by sequentially conjugating two functional moieties onto a β-cyclodextrin scaffold. The thus developed pharmacologically active material may be easily produced into antioxidant and anti-inflammatory nanoparticles, with tunable size. TPCD nanoparticles (TPCD NP) effectively protect macrophages from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in vitro. Consistently, TPCD NP shows superior efficacies in three murine models of inflammatory diseases, with respect to attenuating inflammatory responses and mitigating oxidative stress. TPCD NP can also protect mice from drug-induced organ toxicity. Besides the passive targeting effect, the broad spectrum ROS-scavenging capability contributes to the therapeutic benefits of TPCD NP. Importantly, in vitro and in vivo preliminary experiments demonstrate the good safety profile of TPCD NP. Consequently, TPCD in its native and nanoparticle forms can be further developed as efficacious and safe therapies for treatment of inflammation and oxidative stress-associated diseases.
Keywords: antioxidants; inflammation; nanoparticles; reactive oxygen species; targeted therapy.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
