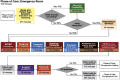
Activity-Based Costing
- PMID: 30357074
- PMCID: PMC6197877
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1672208
Activity-Based Costing
Abstract
Cost allocation for health care professionals can be an enigma within the health care system. Activity-based costing (ABC) is an accounting tool that allocates costs incurred through a company's practice of providing goods and services to the consumer. ABC can provide insight into inefficiencies across the supply chain and unlock excess capacity. This, in turn, can drive services provided toward generating more value for the hospital system. ABC can be tailored to focus upon a unit of measurement that holds value as it pertains to production. With time-driven ABC (Td-ABC), we look to use the advantages of both the fee-for-service and capitation model to transition to a value-based system. Providers are rewarded based on efficiencies and successful outcomes in patient care while disincentivizing poor outcomes and superfluous volume/expenditures. ABC, however, does not come without its own risks and disadvantages, and the user must exercise caution in applying this cost-allocating tool to avoid detriment to its practice. A review of the literature was conducted to analyze the implementation, medical application, and advantages and disadvantages of Td-ABC.
Keywords: accounting; activity-based costing; health care.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan R S, Witkowski M, Abbott M et al. Using time-driven activity-based costing to identify value improvement opportunities in healthcare. J Healthc Manag. 2014;59(06):399–412. - PubMed
-
- Najjar P A, Strickland M, Kaplan R S. Time-driven activity-based costing for surgical episodes. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(01):96–97. - PubMed
-
- Noreen E, Brewer P, Garrison R. New York, NY: McGraw Hill; 2014. Managerial Accounting for Managers; pp. 203–265.
-
- Argyris C, Kaplan R S. Implementing new knowledge: the case of activity-based costing. Account Horiz. 1994;8(03):83–105.
-
- Kaplan R S, Anderson S R.Time-driven activity-based costing Harv Bus Rev 20048211131–138., 150 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous