Long-term Rate of Mesh Sling Removal Following Midurethral Mesh Sling Insertion Among Women With Stress Urinary Incontinence
- PMID: 30357298
- PMCID: PMC6233805
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.14997
Long-term Rate of Mesh Sling Removal Following Midurethral Mesh Sling Insertion Among Women With Stress Urinary Incontinence
Abstract
Importance: There is concern about outcomes of midurethral mesh sling insertion for women with stress urinary incontinence. However, there is little evidence on long-term outcomes.
Objective: To examine long-term mesh removal and reoperation rates in women who had a midurethral mesh sling insertion for stress urinary incontinence.
Design, setting, and participants: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 95 057 women aged 18 years or older who had a first-ever midurethral mesh sling insertion for stress urinary incontinence in the National Health Service hospitals in England between April 1, 2006, and December 31, 2015. Women were followed up until April 1, 2016.
Exposures: Patient and hospital factors and retropubic or transobturator mesh sling insertions.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was the risk of midurethral mesh sling removal (partial or total) and secondary outcomes were reoperation for stress urinary incontinence and any reoperation including mesh removal, calculated with death as competing risk. A multivariable Fine-Gray model was used to calculate subdistribution hazard ratios as estimates of relative risk.
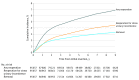
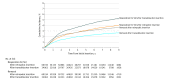
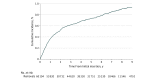
Results: The study population consisted of 95 057 women (median age, 51 years; interquartile range, 44-61 years) with first midurethral mesh sling insertion, including 60 194 with retropubic insertion and 34 863 with transobturator insertion. The median follow-up time was 5.5 years (interquartile range, 3.2-7.5 years). The rate of midurethral mesh sling removal was 1.4% (95% CI, 1.3%-1.4%) at 1 year, 2.7% (95% CI, 2.6%-2.8%) at 5 years, and 3.3% (95% CI, 3.2%-3.4%) at 9 years. Risk of removal declined with age. The 9-year removal risk after transobturator insertion (2.7% [95% CI, 2.4%-2.9%]) was lower than the risk after retropubic insertion (3.6% [95% CI, 3.5%-3.8%]; subdistribution hazard ratio, 0.72 [95% CI, 0.62-0.84]). The rate of reoperation for stress urinary incontinence was 1.3% (95% CI, 1.3%-1.4%) at 1 year, 3.5% (95% CI, 3.4%-3.6%) at 5 years, and 4.5% (95% CI, 4.3%-4.7%) at 9 years. The rate of any reoperation, including mesh removal, was 2.6% (95% CI, 2.5%-2.7%) at 1 year, 5.5% (95% CI, 5.4%-5.7%) at 5 years, and 6.9% (95% CI, 6.7%-7.1%) at 9 years.
Conclusions and relevance: Among women undergoing midurethral mesh sling insertion, the rate of mesh sling removal at 9 years was estimated as 3.3%. These findings may guide women and their surgeons when making decisions about surgical treatment of stress urinary incontinence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Long-term Rate of Mesh Sling Removal Following Midurethral Mesh Sling Insertion Among Women With Stress Urinary Incontinence.Eur Urol. 2019 Apr;75(4):693-694. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.12.020. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 30580901 No abstract available.
-
Re: Long-Term Rate of Mesh Sling Removal following Midurethral Mesh Sling Insertion among Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence.J Urol. 2019 Jul;202(1):22. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000557732.32993.d3. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30925096 No abstract available.
-
Re: Long-term Rate of Mesh Sling Removal Following Midurethral Mesh Sling Insertion Among Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence.Eur Urol. 2019 Oct;76(4):533-534. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.05.019. Epub 2019 May 28. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 31146900 No abstract available.
-
Re: Long-Term Rate of Mesh Sling Removal following Midurethral Mesh Sling Insertion among Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence.J Urol. 2019 Sep;202(3):464. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000574444.84698.38. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31219388 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coyne KS, Kvasz M, Ireland AM, Milsom I, Kopp ZS, Chapple CR. Urinary incontinence and its relationship to mental health and health-related quality of life in men and women in Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Eur Urol. 2012;61(1):88-95. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2011.07.049 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

