Dopamine Signaling Modulates the Stability and Integration of Intrinsic Brain Networks
- PMID: 30357316
- PMCID: PMC6294404
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhy264
Dopamine Signaling Modulates the Stability and Integration of Intrinsic Brain Networks
Abstract
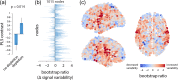
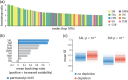
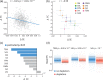
Dopaminergic projections are hypothesized to stabilize neural signaling and neural representations, but how they shape regional information processing and large-scale network interactions remains unclear. Here we investigated effects of lowered dopamine levels on within-region temporal signal variability (measured by sample entropy) and between-region functional connectivity (measured by pairwise temporal correlations) in the healthy brain at rest. The acute phenylalanine and tyrosine depletion (APTD) method was used to decrease dopamine synthesis in 51 healthy participants who underwent resting-state functional MRI (fMRI) scanning. Functional connectivity and regional signal variability were estimated for each participant. Multivariate partial least squares (PLS) analysis was used to statistically assess changes in signal variability following APTD as compared with the balanced control treatment. The analysis captured a pattern of increased regional signal variability following dopamine depletion. Changes in hemodynamic signal variability were concomitant with changes in functional connectivity, such that nodes with greatest increase in signal variability following dopamine depletion also experienced greatest decrease in functional connectivity. Our results suggest that dopamine may act to stabilize neural signaling, particularly in networks related to motor function and orienting attention towards behaviorally-relevant stimuli. Moreover, dopamine-dependent signal variability is critically associated with functional embedding of individual areas in large-scale networks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dopamine precursor depletion impairs structure and efficiency of resting state brain functional networks.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Sep;84:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.12.021. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24412649
-
Catecholaminergic Neuromodulation Shapes Intrinsic MRI Functional Connectivity in the Human Brain.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 27;36(30):7865-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0744-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27466332 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine Modulates the Functional Organization of the Orbitofrontal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 8;37(6):1493-1504. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2827-16.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28069917 Free PMC article.
-
Haloperidol modulates midbrain-prefrontal functional connectivity in the rat brain.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;23(10):1310-9. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23165219
-
Large-scale intrinsic connectivity is consistent across varying task demands.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 10;14(4):e0213861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213861. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30970031 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acute depletion of dopamine precursors in the human brain: effects on functional connectivity and alcohol attentional bias.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Jul;46(8):1421-1431. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-00993-9. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33727642 Free PMC article.
-
A proxy measure of striatal dopamine predicts individual differences in temporal precision.Psychon Bull Rev. 2022 Aug;29(4):1307-1316. doi: 10.3758/s13423-022-02077-1. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Psychon Bull Rev. 2022. PMID: 35318580 Free PMC article.
-
From correlation to communication: Disentangling hidden factors from functional connectivity changes.Netw Neurosci. 2023 Jun 30;7(2):411-430. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00290. eCollection 2023. Netw Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37397894 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the human thalamus on brain-wide information processing.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023 Jul;24(7):416-430. doi: 10.1038/s41583-023-00701-0. Epub 2023 May 26. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37237103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topographic gradients of intrinsic dynamics across neocortex.Elife. 2020 Dec 17;9:e62116. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62116. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33331819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alavash M, Lim SJ, Thiel C, Sehm B, Deserno L, Obleser J. 2018. Dopaminergic modulation of hemodynamic signal variability and the functional connectome during cognitive performance. Neuroimage. 172:341–356. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Crutcher MD. 1990. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 13(7):266–271. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL. 1986. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 9(1):357–381. - PubMed
-
- Avena-Koenigsberger A, Mišić B, Sporns O. 2018. Communication dynamics in complex brain networks. Nat Rev Neurosci. 19(1):17. - PubMed

