Depressive Symptoms at HIV Testing and Two-Year All-Cause Mortality Among Men Who Inject Drugs in Vietnam
- PMID: 30357641
- PMCID: PMC6408284
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-018-2318-8
Depressive Symptoms at HIV Testing and Two-Year All-Cause Mortality Among Men Who Inject Drugs in Vietnam
Abstract
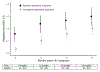
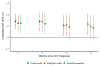
People who inject drugs (PWID) with HIV experience an elevated risk of death. A potentially important determinant of survival is the high burden of depression. This study examined the relationship of depressive symptoms at HIV testing with 2-year all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed HIV-positive PWID in Vietnam. At HIV testing, 141 PWID (42%) experienced severe depressive symptoms, and over the 2 years following diagnosis, 82 PWID (24%) died. Controlling for potential confounders, the 2-year risk of death among those with depressive symptoms was 9.7% (95% CI - 1.2, 20.6%) higher than the risk among those without depressive symptoms. This increased risk of mortality for PWID with depressive symptoms was relatively consistent throughout the 2-year period: at 6, 12, and 18 months, the risk difference was 12.6% (5.5-19.7%), 13.9% (4.6-23.2%), and 11.0% (0.9-21.1%), respectively. HIV diagnosis may provide an important opportunity for depression screening and treatment, subsequently improving survival in this key population.Trial registry: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01689545.
Keywords: Depression; HIV; Injection drug use; Mortality; Vietnam.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. How AIDS changed everything - MDG6: 15 years, 15 lessons of hope from the AIDS response. 2015. Available from: http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2015/MDG6_15years-15lessons...
-
- Dutta A, Wirtz A, Stanciole A, Oelrichs R, Semini I, Baral S, et al. The global HIV epidemics among people who inject drugs. Washington DC: World Bank; 2013. Available from: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ecn&AN=1386909&sit...
-
- Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Phillips B, Wiessing L, Hickman M, Strathdee SA, et al. Global epidemiology of injecting drug use and HIV among people who inject drugs: a systematic review. Lancet. 2008; 372: 1733–45. - PubMed
-
- UN Joint Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). The Gap Report. 2014. Available from: http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2014/20140716_UNAIDS_gap_re...
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

